Zoology - Basic concepts of immunology | 12th Zoology : Chapter 8 : Immunology
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 8 : Immunology
Basic concepts of immunology
Basic
concepts of immunology
Immunology is the study of immune
system. This system protects an indvidual from various infective agents. It
refers to all the mechanisms used by the body for protection from environmental
agents that are foreign to the body.
When the immune system
does not function efficiently in an individual, it leads to infection causing
disease. The overall ability of body to fight against the disease causing
pathogen is called immunity. It is also called disease resistance and
the lack of immunity is known as susceptibility. Immunity is highly specific.
Normally many of the
responses of the immune system initiate the destruction and elimination of
invading organisms and any toxic molecules produced by them. These immune
reactions are destructive in nature and are made in response only to molecules
that are foreign to the host and not to those of host itself. This ability to
distinguish foreign molecules from self is another fundamental feature of the
immune system. However, occasionally, it fails to make its distinction and
reacts destructively against the host's own molecules; such autoimmune diseases
can be fatal to the organism.
Almost all the macromolecules e.g.proteins,
polysaccharides, nucleic acids, etc., as long as they are foreign
to recipient organism can
induce immune response. Any substance capable of eliciting
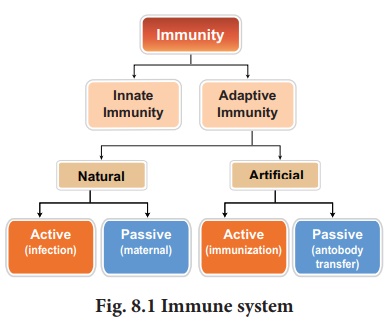
immune response is called an ANTIGEN (ANTIbody GENerator). There are two broad
classes of immunity responses namely, innate immunity and acquired immunity (Fig.
8.1).
Related Topics