Immunology - Immune responses | 12th Zoology : Chapter 8 : Immunology
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 8 : Immunology
Immune responses
Immune
responses
The immune responses may
be primary or secondary (Table 8.3).
Primary immune response
The primary immune
response occurs when a pathogen comes in contact with the
During this, the immune
system has to learn to recognize the
antigen, produce antibody against it and eventually produce
memory lymphocytes. The primary immune response is slow and short-lived.
Secondary immune
The secondary immune
response occurs when a person is exposed to the same antigen again. During this
time, immunological memory has been established and the immune system can start
producing antibodies immediately.
Within hours after
recognition of the antigen, a new army of plasma cells are generated. Within 2
to 3 days, the antibody concentration in the blood rises steeply to reach much
higher level than primary response. This is also called as “booster response”.
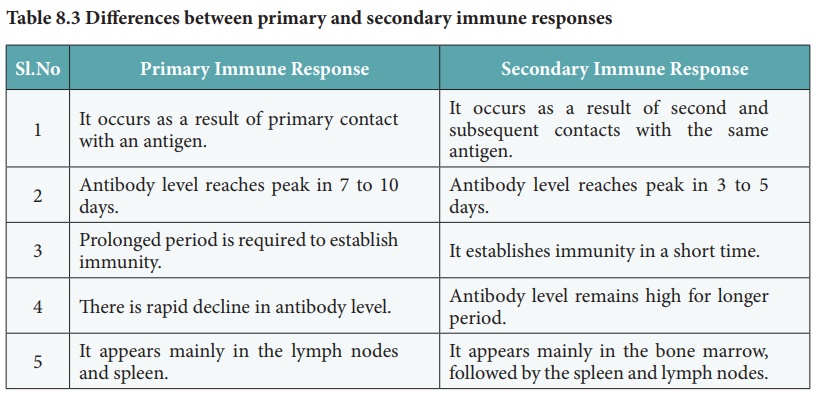
Primary Immune Response
1. It occurs as a result of primary contact with an antigen.
2. Antibody level reaches peak in 7 to 10 days.
3. Prolonged period is required to establish immunity.
4. There is rapid decline in antibody level.
5. It appears mainly in the lymph nodes and spleen.
Secondary Immune Response
1. It occurs as a result of second and subsequent contacts with the same antigen.
2. Antibody level reaches peak in 3 to 5 days.
3. It establishes immunity in a short time.
4. Antibody level remains high for longer period.
5. It appears mainly in the bone marrow, followed by the spleen and lymph nodes.
Related Topics