Chapter: Biochemistry: Living Cell
Types of Living cells
Types of cells
Two general types are recognised in nature.
They are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
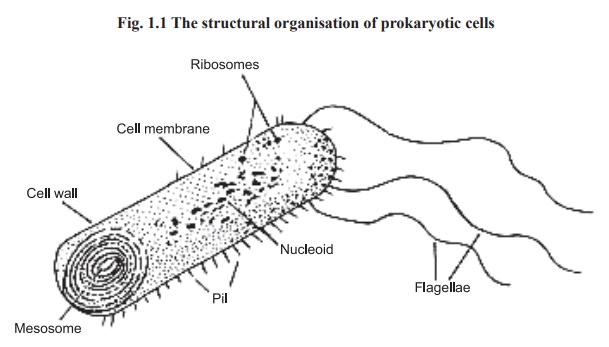
Prokaryotic cells
Prokaryotes were the first cells to arise in
biological evolution. They are very small and simple having only a single
membrane. The cell membrane, is usually surrounded by a rigid cell wall.
They are devoid of nucleus and membranous
organelles such as mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum etc. (Fig. 1.1).
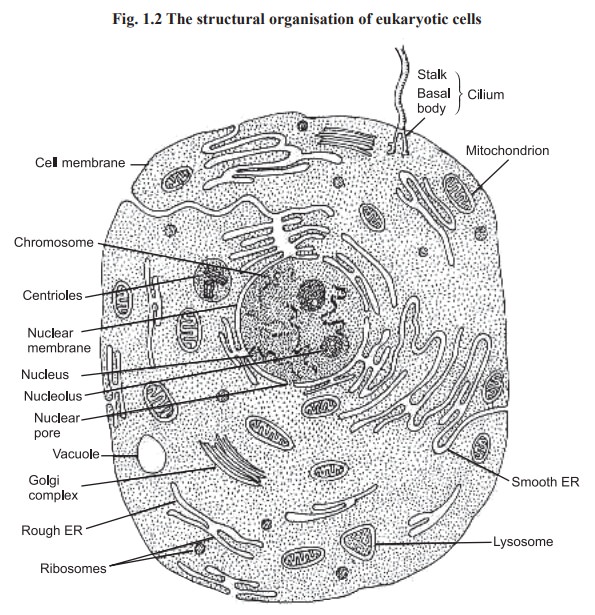
Eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic cells are presumably derived from
prokaryotes. They are much larger and much more complex than prokaryotic cells
(Fig. 1.2).
They have nucleus and membrane bound
subcellular organelles. Many of their metabolic reactions are segregated within
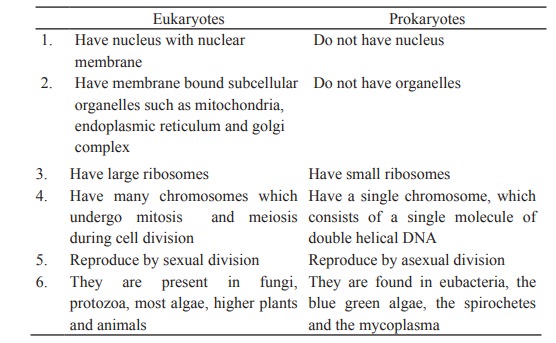
structural compartments. The significant differences between prokaryotic and
enkaryotic cells are:
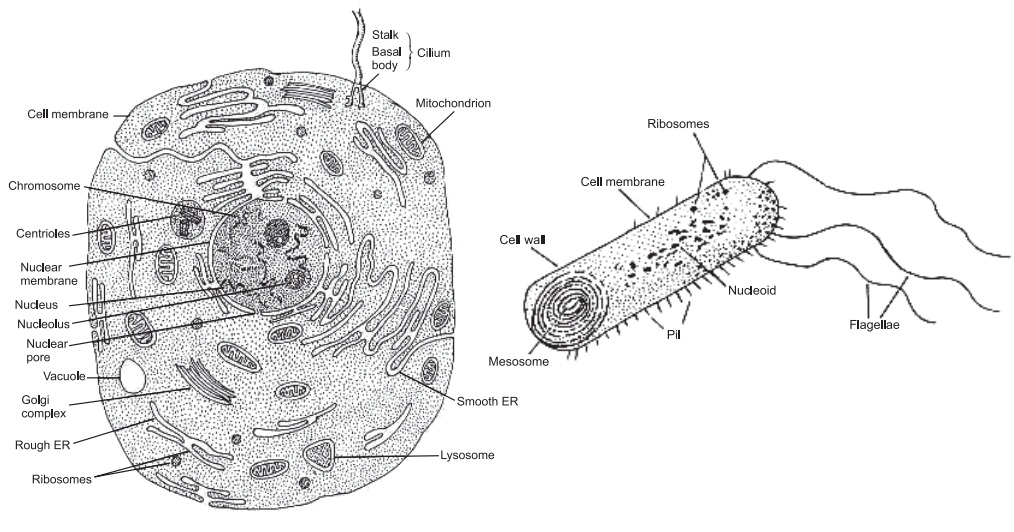
The eukaryotic cell structure is composed of
(i) cell membrane, (ii) nucleus (iii) mitochondria (iv) endoplasmic reticulum
(v) golgi apparatus (vi) ribosomes (vii) lysosomes and others. These
specialised structural units are called as subcellular organnelles.
Biochemistry today is increasingly concerned with the structure of cells and
their organelles.
Related Topics