Chapter: Biochemistry: Living Cell
Nucleus and its Functions
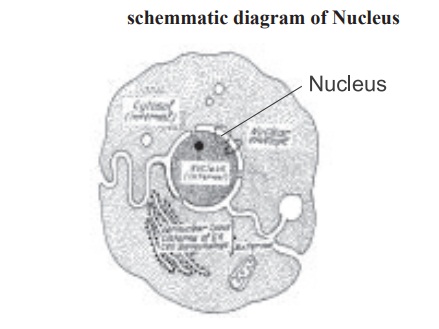
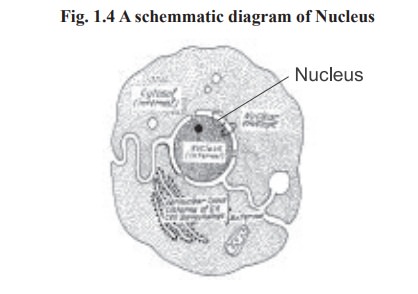
Nucleus
Nucleus is the heaviest particulate component
of the cell. Except matured mammalian erythrocytes, nucleus is found in almost
all cells. The nucleus about 4-6µm in diameter is surrounded by a perinuclear
envelope. At various position the outer membrane of the envelope fuses with the
inner membrane to form pores (Fig. 1.4). Nuclear pores provide continuity
between the cytosol and the contents of the nucleus (nucleoplasm). The electron
microscope reveals that the nuclear content consist of granular or fibrillar
structures. The nucleolus, a discrete body within the nucleus, contains
ribonucleic acids (RNA). The most important component of the nucleus is an
organised clumps of threadwork known as chromatin which is distributed
throughout the nucleus and contains most of the cellular deoxy ribonucleic
acids (DNA). Immediately before the cell division the chromatin organises into
simple thread like structures known as chromosomes which will eventually be
distributed equally to each daughter cell.
Functions
Take part in cell division Contain DNA molecules which are heriditary carriers.
Related Topics