Chapter: Biochemistry: Living Cell
Body Fluids
Body Fluids
Cerebrospinal fluid and lymph are other
important body fluids which are devoid of red blood cells and so they look
colourless.
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
CSF is formed by the choroid plexus of the
brain and is an ultrafiltrate of the plasma. It is present in the central
ventricles, spinal canal and subarachnoid spaces. The total volume of CSF is
100-150ml.
haematopoiesis
Properties
a clear, colourless and transparent fluid with
a specific gravity of 1.003 to 1.008. It is alkaline and has the same pH as
that of blood (7.35 to 7.40).
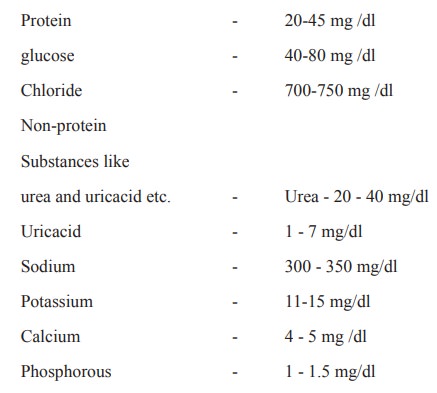
Composition
It’s composition is more or less similar to
that of plasma without the colloids
Function
It acts as a protective jacket for the brain
and spinal cord and maintains a uniform pressure on the nervous structures. It
acts as a reservoir to regulate the contents of the cranium. To a limited
extent it act as a medium for nutrient exchange in the nervous system.
CSF in diseases
The composition of CSF is altered in the
following diseased conditions in human beings.

Lymph
The term ‘lymph’ denotes a fluid not only
present in the lymphatic vessels but also the fluid which bathes in the cells
and the tissue.
It resembles plasma in its components and their
composition which can permeate the capillary wall but there are some
differences in electrolyte concentrations.
About 2 litres of lymph are drained into the
blood stream per day. Lymph flow is very slow. The protein present in entire
plasma in an adult human is about 210 gm. About 1/3rd of this leaks out into
the lymph through the interstitial fluid and is returned to the blood at the
thoracic duct. If the thoracic lymph is drained off, the concentration of
plasma proteins fall and the blood volume decreases
Functions
Lymph is the main route of absorption of long
chain fatty acids, partially digested fats, diacyl glycerol and cholesterol
from the intestine and their transport via the thoracic duct. Lymph also helps
to keep the tissues from drying up by maintaining contact with the interstitial
fluids.
Related Topics