Chapter: Biochemistry: Living Cell
Mitochondria and its Functions
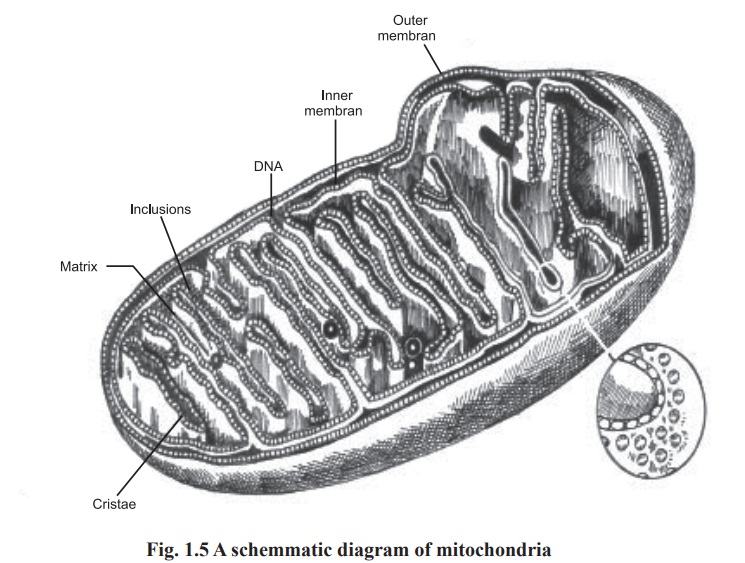
Mitochondria
These are the largest particulate components of
the cytoplasm and represent upto 15% -20% of the dry weight of the cell. They
vary in shape (spherical, filamentous, sausage shaped) and size (0.5 to 3μ long
0.1 to 0.6μ wide).The number varies with the size and energy requirements of
the cell. For eg. flight muscles in birds contain rich amount of mitochondria
when compared to any other parts of the body
Electron microscopic studies show that a
mitochondrion has two membranes inner and outer which are separated from each
other by 50 to 100oA. The outer and inner membranes differ in lipid composition
and in enzyme content.
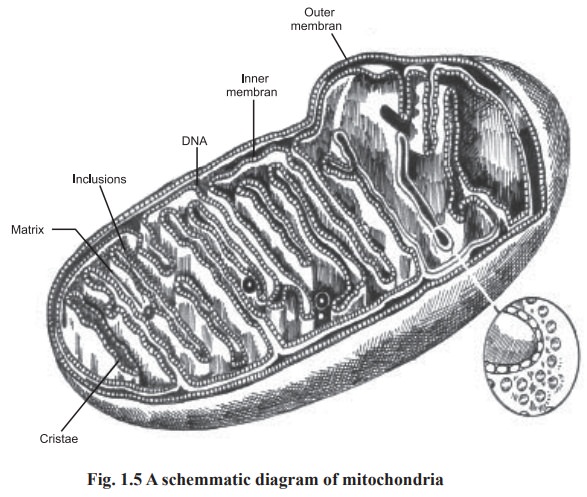
The inner membrane is very much folded to form
shelf - like structures of varying width. These shelf - like structures, known
as internal ridgs or cristae, extent into matrix of the mitochondrion
structure. Thus two structurally different space can be distinguished, the
intracristae space and the matrix space (Fig. 1.5). The matrix space is rich in
enzymes. The inner membrane shows the existance of knob like structures, which
are proteins involved in biological oxidations.
Functions
: The mitochondria are the ‘power houses’ of the
cell, where carbohydrates, lipids and
amino acids are oxidised to CO2 and H2O by molecular
oxygen, and the energy set free is stored in the form of adenosine triphosphate
(ATP). The enzymes involved in this energy conversion are located in the inner
membrane.
Related Topics