Chapter: Electrical machines : Three Phase Induction Motor
Types and Construction of Three Phase Induction Motor
Types and Construction of Three Phase Induction Motor
Three phase induction motors are constructed into two major types:
1. Squirrel cage Induction Motors
2. Slip ring Induction Motors
1. Squirrel cage Induction Motors
(a) Stator Construction
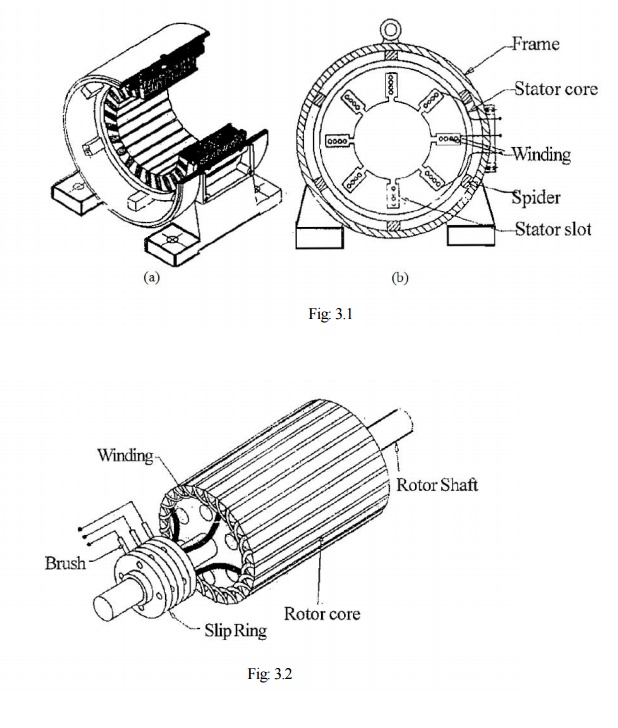
The induction motor stator resembles the stator of a revolving field, three phase alternator. The stator or the stationary part consists of three phase winding held in place in the slots of a laminated steel core which is enclosed and supported by a cast iron or a steel frame as shown in Fig: 3.1(a).
The phase windings are placed 120 electrical degrees apart and may be connected in either star or delta externally, for which six leads are brought out to a terminal box mounted on the frame of the motor. When the stator is energized from a three phase voltage it will produce a rotating magnetic field in the stator core.
(b) Rotor Construction
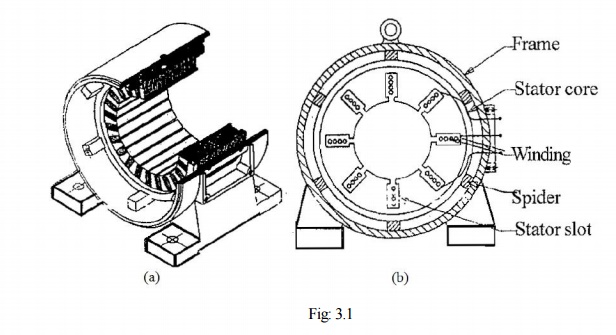
The rotor of the squirrel cage motor shown in Fig: 3.1(b) contains no windings. Instead it is a cylindrical core constructed of steel laminations with conductor bars mounted parallel to the shaft and embedded near the surface of the rotor core.
These conductor bars are short circuited by an end rings at both end of the rotor core. In large machines, these conductor bars and the end rings are made up of copper with the bars brazed or welded to the end rings shown in Fig: 3.1(b).In small machines the conductor bars and end rings are sometimes made of aluminium with the bars and rings cast in as part of the rotor core. Actually the entire construction (bars and end-rings) resembles a squirrel cage, from which the name is derived.
The rotor or rotating part is not connected electrically to the power supply but has voltage induced in it by transformer action from the stator. For this reason, the stator is sometimes called the primary and the rotor is referred to as the secondary of the motor since the motor operates on the principle of induction and as the construction of the rotor with the bars and end rings resembles a squirrel cage, the squirrel cage induction motor is used.
The rotor bars are not insulated from the rotor core because they are made of metals having less resistance than the core. The induced current will flow mainly in them. Also the rotor bars are usually not quite parallel to the rotor shaft but are mounted in a slightly skewed position. This feature tends to produce a more uniform rotor field and torque. Also it helps to reduce some of the internal magnetic noise when the motor is running.
(c) End Shields
The function of the two end shields is to support the rotor shaft. They are fitted with bearings and attached to the stator frame with the help of studs or bolts attention.
2. Slip ring Induction Motors
(a) Stator Construction
The construction of the slip ring induction motor is exactly similar to the construction of squirrel cage induction motor. There is no difference between squirrel cage and slip ring motors.
(b) Rotor Construction
The rotor of the slip ring induction motor is also cylindrical or constructed of lamination.
Squirrel cage motors have a rotor with short circuited bars whereas slip ring motors have wound rotors having "three windings" each connected in star.
The winding is made of copper wire. The terminals of the rotor windings of the slip ring motors are brought out through slip rings which are in contact with stationary brushes as shown in Fig: 3.2.
THE ADVANTAGES OF THE SLIPRING MOTOR ARE
• It has susceptibility to speed control by regulating rotor resistance.
• High starting torque of 200 to 250% of full load value.
• Low starting current of the order of 250 to 350% of the full load current.
Hence slip ring motors are used where one or more of the above requirements are to be met.
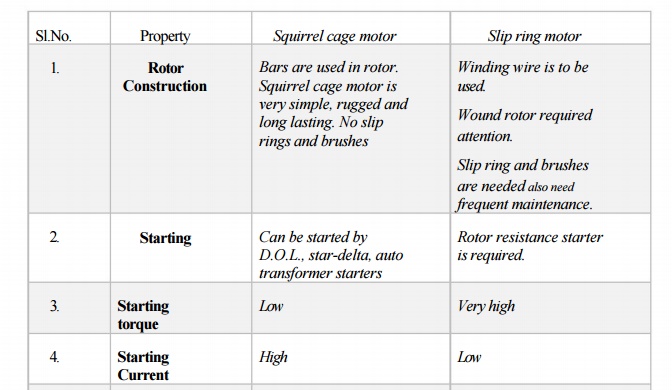
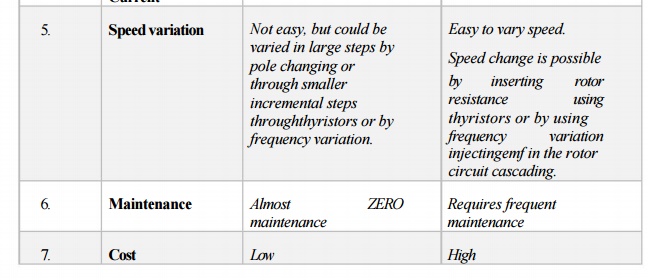
3. Comparison of Squirrel Cage and Slip Ring Motor
Related Topics