Chapter: Linear Integrated Ciruits : Application of ICs
Transformer Operation
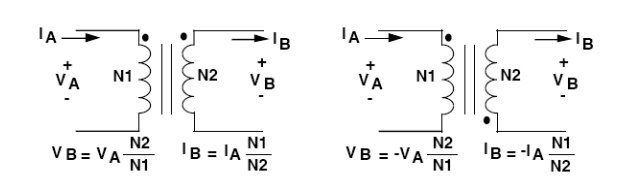
Transformer Operation:
A
transformer is a device that has two or more magnetically-coupled windings. The
basic operation is shown in Figure. The action of a transformer is such that a
time-varying (AC) voltage or current is transformed to a higher or lower value,
as set by the transformer turns ratio. The transformer does not add power, so
it follows that the power (V X I) on either side must be constant. That is the
reason that the winding with more turns has higher voltage but lower current,
while the winding with less turns has lower voltage but higher current. The dot
on a transformer winding identifies its polarity with respect to another
winding, and reversing the dot results in inverting the polarity Example of
Transformer Operation: An excellent example of how a transformer works can be
found under the hood of your car, where a transformer is used to generate the
40 kV that fires car‘s spark plugs.
Related Topics