Chapter: Linear Integrated Ciruits : Application of ICs
Boost Regulator
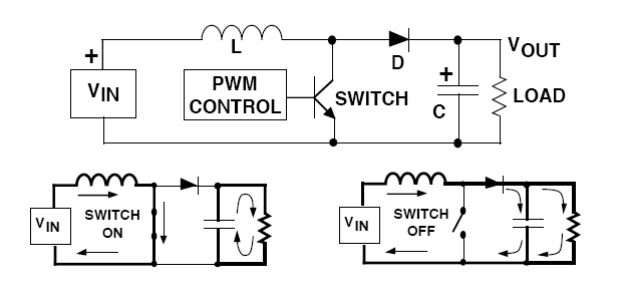
Boost Regulator:
The Boost
regulator takes a DC input voltage and produces a DC output voltage that is higher
in value than the input (but of the same polarity). The Boost regulator is
shown in Figure, along with details showing the path of current flow during the
switch on and off time. Whenever theswitch is on, the input voltage is forced
across the inductor which causes the current through it to increase (ramp up).
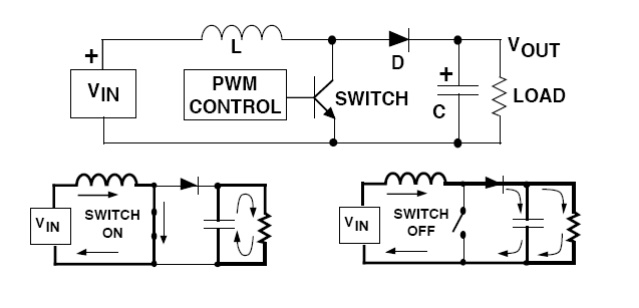
When the
switch is off, the decreasing inductor current forces the "switch"
end of the inductor to swing positive. This forward biases the diode, allowing
the capacitor to charge up to a voltage that is higher than the input voltage.
During steady-state operation, the inductor current flows into both the output
capacitor and the load during the switch off time. When the switch is on, the
load
current
is supplied only by the capacitor.
Output Current and Load power:
An
important design consideration in the Boost regulator is that the output load
current and the switch current are not equal, and the maximum available load
current is always less than the current rating of the switch transistor. It
should be noted that the maximum total power available for conversion in any
regulator is equal to the input voltage multiplied times the maximum average
input current (which is less than the current rating of the switch transistor).
Since the output voltage of the Boost is higher than the input voltage, it
follows that the output current must be lower than the input current.
Related Topics