Chapter: Essential Anesthesia From Science to Practice : Applied physiology and pharmacology : Anesthesia and the lung
Tissue oxygenation
Tissue oxygenation
Once we get both air and blood into the lungs, oxygen must traverse the alve-olar membrane. Oxygen diffusion across this membrane depends on the Fick2 Equation:
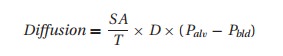
where SA = surface area of the alveoli (decreased in emphysema); T= membrane thickness (increased with pulmonary edema), D= diffusion constant for a given gas,3 and Palv−Pbld= the gas pressure difference across the membrane dividing alveolus from blood.
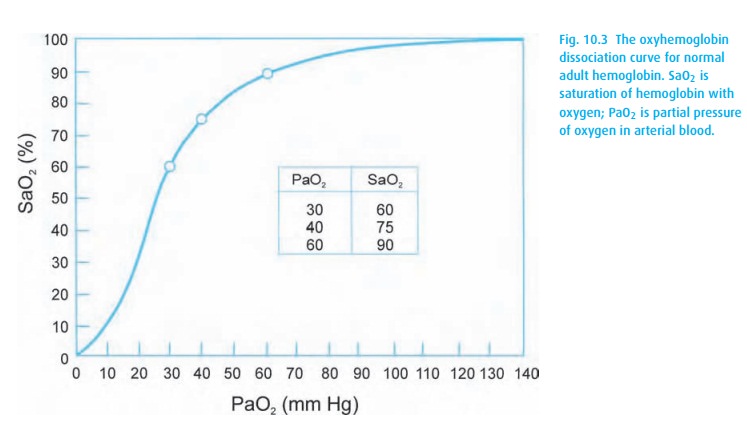
After traversing the alveolar and capillary wall membrane, oxygen dissolves in plasma (not much; 0.003 × PaO2) and binds with hemoglobin (a bunch), and the arterial oxygen content (CaO2) becomes
C aO2=1.34×[Hgb]× SaO2+0.003× PaO2
where CaO2= volume of oxygen in 100 mL blood, Hgb = hemoglobin concentra-tion, and SaO2= arterial hemoglobin saturation with oxygen.
Related Topics