Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 1 : The Living World
Three Domains of life
Three Domains
of life
Three
domain classification was proposed by Carl
Woese (1977) and his co--workers. They classified organisms based on the
difference in 16S rRNA genes. The three domain system adds the taxon ‘domain’
higher than the kingdom. This system emphasizes the separation of Prokaryotes
into two domains, Bacteria and Arachaea, and all the eukaryotes are placed into
the domain Eukarya. Archaea appears to have more in common with the Eukarya
than the Bacteria. Archaea differ from bacteria in cell wall
composition and differs from bacteria and eukaryotes in membrane composition
and rRNA types.
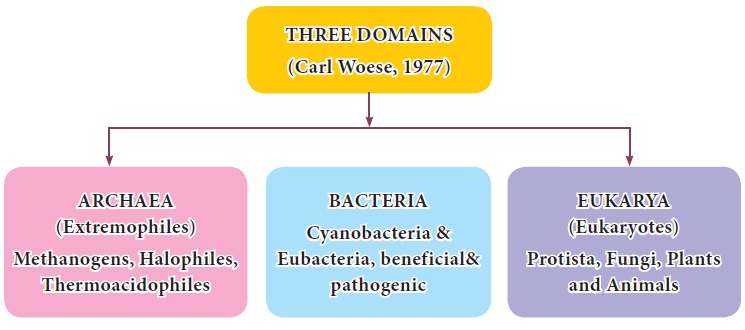
1. Domain Archaea
This
domain includes single celled organisms, the prokaryotes which have the ability
to grow in extreme conditions like volcano vents, hot springs and polar ice
caps, hence are also called extremophiles.
They are capable of synthesizing their food without sunlight and oxygen by
utilizing hydrogen sulphide and other chemicals from the volcanic vents. Some
of the them produced methane (methanogens), few live in salty environments
(Halophiles) and are thermoacidophiles which thrive in acidic environments and
at high temperatures.
2. Domain Bacteria
Bacteria
are prokaryotic, their cells have no definite nucleus and DNA exists as a
circular chromosomes and do not have histones associated with it. They do not
possess membrane bound organelles except for ribosome (70S type). Their cell
wall contains peptidoglycans. Many are decomposers, some are photo-synthesizers
and few cause diseases. There are beneficial probiotic bacteria and harmful pathogenic
bacteria which are diversely populated. Cyanobacteria are photosynthetic blue
green algae which produce oxygen. These had played a key role in the changes of
atmospheric oxygen levels from anaerobic to aerobic during the early geologic
periods.
3. Domain Eukarya (Eukaryotes)
Eukaryotes
are animals which have true nucleus and membrane bound organelles. DNA in the
nucleus is arranged as a linear chromosome with histone proteins, ribsosomes of
80S type in the cytosol and 70S type in the chloroplast and mitochondria.
Animals in this domain are classified under kingdoms, namely, Protista, Fungi,
Plantae and Animalia.
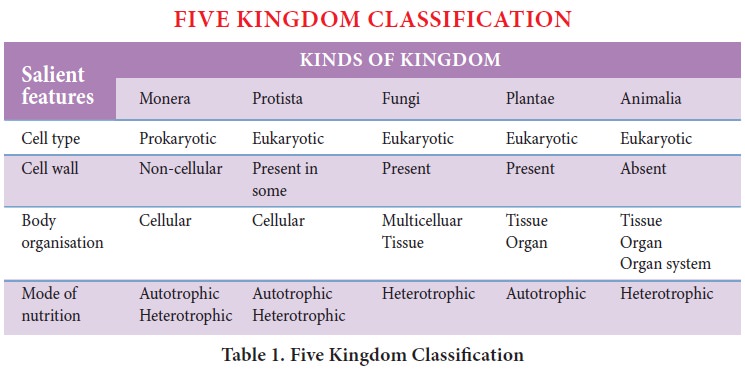
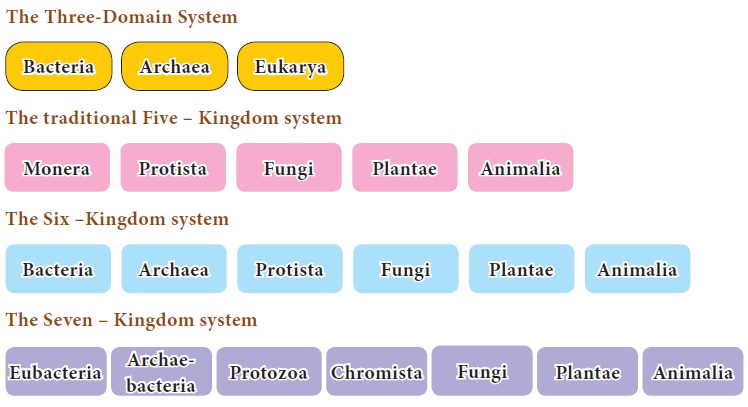
In 1987, Cavalier-Smith revised the six kingdom system to Seven Kingdom system. The concept of super kingdom was introduced and revised to seven kingdom classification.
The classification is divided into two
Super Kingdoms (Prokaryota and Eukaryota) and seven kingdoms, two Prokaryotic
Kingdoms (Eubacteria and Archaebacteria) and five Eukaryotic Kingdoms
(Protozoa, Chromista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia).
Related Topics