Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 1 : The Living World
Taxonomic hierarchy
Taxonomic hierarchy
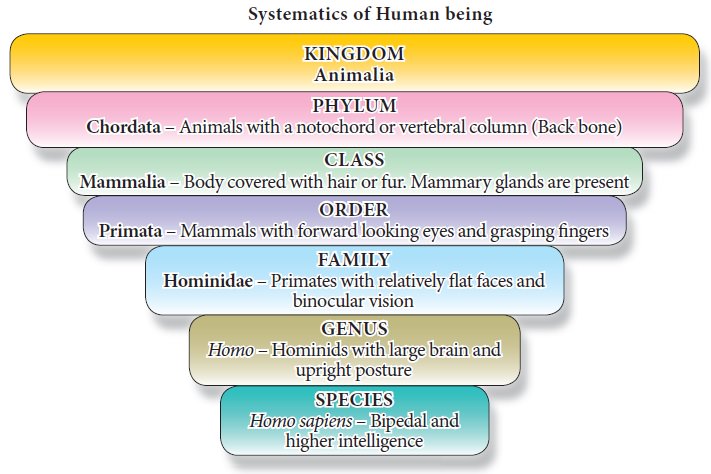
In biological classification, the taxonomical hierarchy includes seven major categories namely kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species and other intermediate categories such as subkingdom, grade, division, subdivision, subphylum, superclass, subclass, superorder, suborder, superfamily, subfamily and subspecies.
Species
Species
is the basic unit of classification in the taxonomic hierarchial system. It is
a group of animals having similar morphological features (traits) and is
reproductively isolated to produce fertile offspring. There are some
exceptional animals which can produce sterile
offspring because of mating with closely related species (Figure 1.2).

Genus: It is a group of closely related
species which have evolved from a common
ancestor. In some genus there is only one species which is called as monotypic genus (e.g. Red panda is the
only species in the genus Ailurus : Ailurus fulgens) (Figure 1.3). If there
are more than one species in the genus it is known as polytypic genus, for example ‘cats’ come under the Genus Felis, which has a number of closely
related species, Felis domestica
(domestic cat), Felis margarita
(jungle cat). Felis silvestris (wild
cat)

Family: It is a taxonomic category which
includes a group of related genera with less similarity as compared to genus and species. For example, the
family Felidae includes the genus Felis
(cats) and the genus Panthera (lions,
tigers, leopards).
Order: This category includes an
assemblage of one or more related families which show few common features. One or more similar families are grouped
together to form an order. For example, family Canidae and Felidae are
placed in the order Carnivora.
Class: This category includes one or
more related orders with some common characters.
For example order Primata comprising monkeys, apes and man is placed in the
Class Mammalia, along with the order Carnivora which includes dogs and cats.
Phylum: The group of classes with similar
distinctive characteristics constitute a
phylum. The classes Pisces, Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves and Mammalia
constitute the next higher category, phylum Chordata. These classes share some
common features like presence of a notochord and a dorsal tubular nerve cord
hence included in the phylum Chordata.
Kingdom: All living animals belonging to
various phyla are included in the Kingdom
Animalia and it is the top most of the taxonomic hierarchy.
Related Topics