Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 1 : The Living World
Taxonomy and Systematics
Taxonomy and
Systematics
Taxonomy
(G. taxis- arrangement ; nomos-law) is the science of arrangement
of living organisms along with classification, description, identification, and
naming of organisms which includes all flora and fauna including microorganisms
of the world. The word taxonomy was coined by Augustin Pyramus de Candole (1813). Taxonomy is a theoretical study
of classification with well defined principles, rules and procedures. Aristotle is called the father of
taxonomy (classical) and Carolus Linnaeus is the father of modern taxonomy.
Systematics (G. System/sequence)
The
objectives of taxonomy and systematics are very similar; their goal is to
classify organisms with stipulated rules. The main criteria of systematics is
identifying, -describing, naming, arranging, preserving and documenting the
organisms. Apart from the above said features, evolutionary history of the
species and the environmental adaptations and interrelationship between species
are also being investigated in systematics.
History of Classification
Early
classification of organisms were based on only two criteria, beneficial or
harmful animals. An ancient classification system recognized 5 animal groups -
domestic, wild, creeping, flying and sea animals. Initially the classification
was based on organism’s fundamental characteristics such as the habitat and
morphology only.
Aristotle (384 to 322 BC), was the first to
classify all animals in his History of
Animals (Historia Animalium in Latin). He attempted a basic
classification of all living
organisms into Plants and Animals. Animals were classified based on locomotion;
walking (terrestrial), flying (aerial) and swimming (aquatic). Based on the
presence or absence of red blood he classified the animals into two as Enaima with blood and those without
blood as Anaima.
Aristotle’s
classification system had limitations and many organisms were not fitting into
his classification. For example, the tadpoles of frogs are born in water and
have gills but when they metamorphosed into adult frogs they have lungs and can
live both in water and on land. How to classify frogs and where to place them?
Aristotle classified organisms based on locomotion, hence, birds, bats, and
flying insects were grouped together just by observing one single
characteristic feature, the flying ability. On the contrary to the above said
example, the ostrich, emu and penguin are all birds but cannot fly. So
Aristotle would not have classified them as birds. In spite of these
limitations Aristotle’s classification system was followed for more than 2000
years upto 1700.
After
Aristotle, his student Theophrastus
(372-287 BC) continued his research on the classification of plants, and he was
known as the “Father of Botany.” There was a huge gap till 16th century, then
the English naturalist John Ray (1627–1705)
wrote several important works through his life. His most important contribution
was the establishment of species as the ultimate unit of taxonomy. In 1682 he
published the Methodus Plantarum Nova,
which contained about 18,000 plant species, a result of a
relatively narrow species concept. His complicated classification was based
on many combined characters, as opposed to earlier taxonomists. John Ray also
aimed at publishing a complete system of nature, which included works on
mammals, reptiles, birds, fishes and insects. The Swedish biologist Carolus Linnaeus (1707 - 1788) father
of modern taxonomy and founder of modern systematics developed a scientific
system of taxonomy and binomial nomenclature, which is still (with
modifications) in use.
Aristotle
to Linnaeus employed easily observable single to few traits for classificatio1n
of organisms. With increased knowledge of the several biological domains, many
characters were considered for classifying organisms. This represented the
phase of classical taxonomy which was based on overall similarities or
affinities derived from morphology, anatomy and embryology of organisms. A
modification of this system is the numerical taxonomy, which evolved in the
1950s. This system evaluates the resemblances and differences through
statistical methods followed by computer analyses to establish the numerical
degree of relationship among individuals. Later on biologists
initiated studies on the evolutionary and genetic relationships among organisms,
which led to the emerge of phylogenetic
classification or cladistics-. It is an evolutionary classification based
on how a common ancestry was shared.
Cladistic classification -summarizes the genetic differences between all
species in the ‘phylogenetic tree’. Ernst Haeckal introduced the method of
representing evolutionary relationships with the help of a tree diagram known
as cladogram.
This
system of classification takes into account ancestral characters (traits of
basic body design which would be in the entire group) and derived characters
(traits whose structure and functions differs from those of ancestral
characters). One or more derived characters which appeared during evolution
resulted in the formation of new subspecies. In a cladogram each evolutionary
step produces a branching and all the
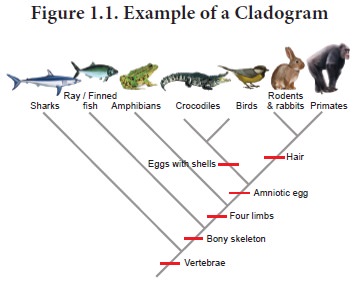
Arranging organisms on the basis
of their similar or derived characters which differ from the ancestral
characters produced a phylogenetic tree or cladogram (Figure 1.1).
Depending
on the system of classification, organisms were classified into two or three
kingdoms. Later into four, five, six and now into seven kingdoms. R.H.Whittaker
(1969) proposed the Five kingdom
Classification, the Kingdoms defined by him were Monera, Protista, Fungi,
Plantae, and Animalia based on the cell structure, mode of nutrition, mode of
reproduction and phylogenetic relationships. Table 1. gives a comparative
account of different characteristics of the five kingdoms.
Classification
has come a long way and now takes into an account even molecular level DNA and
RNA identification. The advancement in molecular techniques and biochemical
assays has led to a new classification - The “Three Domain” classification.
Related Topics