Chapter: Clinical Dermatology: The skin in systemic disease
The skin in sarcoidosis
The skin
in sarcoidosis
About
one-third of patients with systemic sarcoidosis have skin lesions; it is also
possible to have cutaneous sarcoidosis without systemic abnormalities. The most
important skin changes are as follows.
1
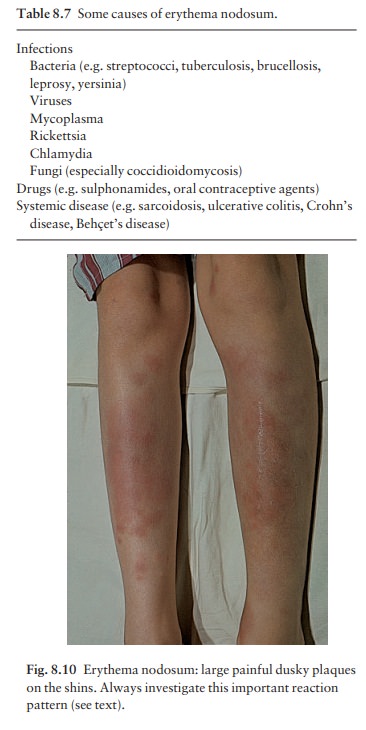
Erythema nodosum (see Fig. 8.10). This occurs in
theearly stages of sarcoidosis, especially in young women.
2 Scar sarcoidosis.
Granulomatous lesions arisingin longstanding scars should raise suspicions of
sarcoidosis.
3 Lupus pernio.
Dusky infiltrated plaques appearon the nose and fingers, often in association
with sarcoidosis of the upper respiratory tract.
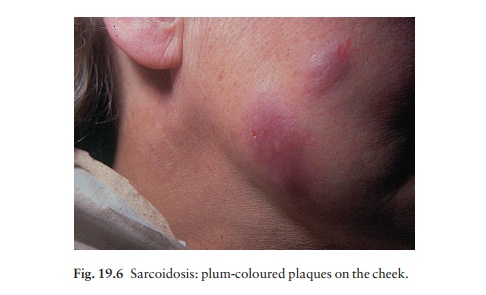
4 Papular, nodular and plaque forms(Fig.
19.6).These brownish-red, violaceous, or hypopigmented papules and plaques are
indolent although often symptom-free. Sometimes they are annular. They vary in
number, size and distribution. Intralesional and topical corticosteroids are
sometimes helpful and hydroxychloroquine
has been used successfully. Chronic lesions respond poorly to any line
of treatment short of systemic steroids, which are usually best avoided if
involvement is confined to the skin.
Related Topics