Chapter: Java The Complete Reference : The Java Library : java.util : More Utility Classes
The ResourceBundle, ListResourceBundle, and PropertyResourceBundle Java Classes
The ResourceBundle, ListResourceBundle, and
PropertyResourceBundle Classes
The java.util package includes three
classes that aid in the internationalization of your program. The first is the
abstract class ResourceBundle. It
defines methods that enable you to manage a collection of locale-sensitive
resources, such as the strings that are used to label the user interface
elements in your program. You can define two or more sets of translated strings
that support various languages, such as English, German, or Chinese, with each
translation set residing in its own bundle. You can then load the bundle
appropriate to
the
current locale and use the strings to construct the program’s user interface.
Resource
bundles are identified by their family
name (also called their base name).
To the family name can be added a two-character lowercase language code which specifies the language. In this case, if a
requested locale matches the language code, then that version of
the
resource bundle is used. For example, a resource bundle with a family name of SampleRB could have a German version
called SampleRB_de and a Russian
version called SampleRB_ru. (Notice
that an underscore links the family name to the language code.) Therefore, if
the locale is Locale.GERMAN, SampleRB_de will be used.
It is
also possible to indicate specific variants of a language that relate to a
specific country by specifying a country
code after the language code. A country code is a two-character uppercase
identifier, such as AU for Australia
or IN for India. A country code is
also preceded by an underscore when linked to the resource bundle name. A
resource bundle that has only the family name is the default bundle. It is used
when no language-specific bundles are applicable.
The
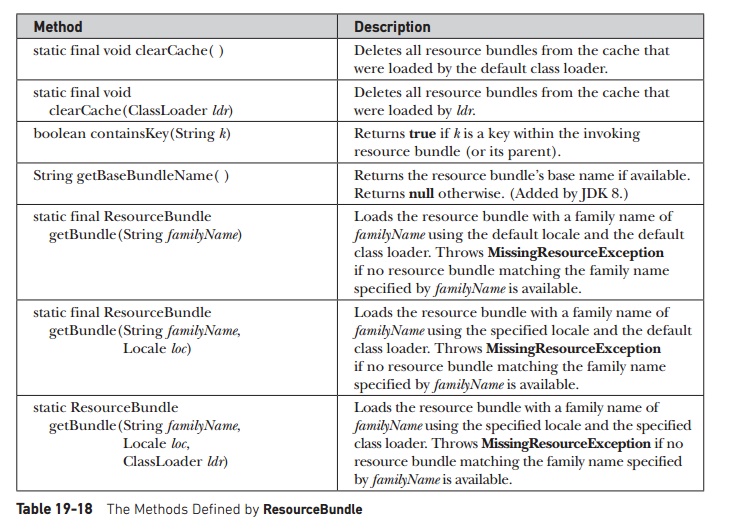
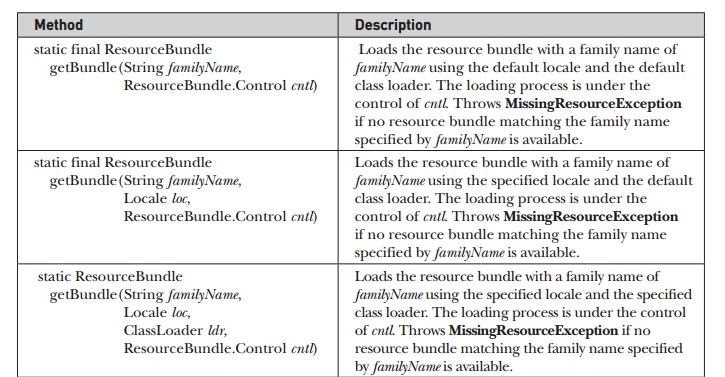
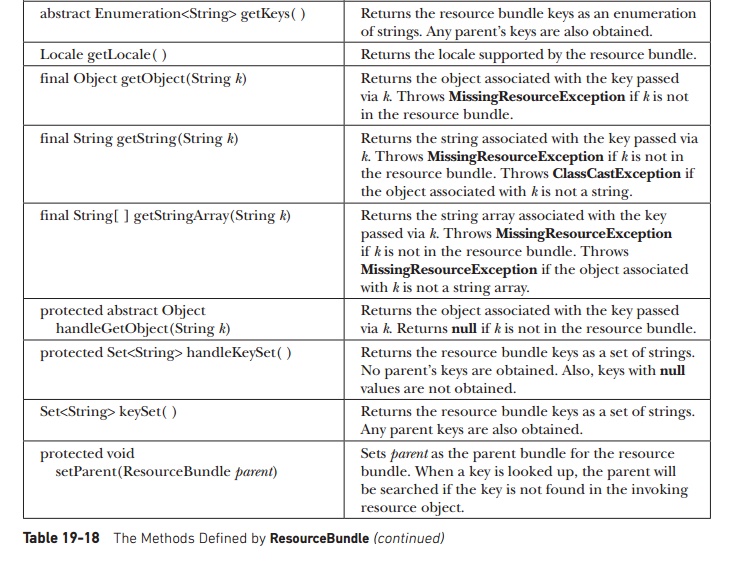
methods defined by ResourceBundle
are summarized in Table 19-18. One important point: null keys are not allowed and several of the methods will throw a NullPointerException if null is passed as the key. Notice the
nested class ResourceBundle.Control.
It is used to control the resource-bundle loading process.
There
are two subclasses of ResourceBundle.
The first is PropertyResourceBundle,
which manages resources by using property files. PropertyResourceBundle adds no methods of its own. The second is
the abstract class ListResourceBundle,
which manages resources in an array of key/value pairs. ListResourceBundle adds the method getContents( ), which all subclasses must implement. It is shown
here:
protected
abstract Object[ ][ ] getContents( )
It
returns a two-dimensional array that contains key/value pairs that represent
resources. The keys must be strings. The values are typically strings, but can
be other types of objects. Here is an example that demonstrates using a
resource bundle. The resource bundle
has the
family name SampleRB. Two resource
bundle classes of this family are created by extending ListResourceBundle. The first is called SampleRB, and it is the default bundle (which uses English). It is
shown here:
import java.util.*;
public class SampleRB extends
ListResourceBundle {
protected Object[][]
getContents() {
Object[][] resources = new
Object[3][2];
resources[0][0] = "title";
resources[0][1] = "My Program";
resources[1][0] =
"StopText"; resources[1][1] = "Stop";
resources[2][0] =
"StartText"; resources[2][1] = "Start";
return resources;
}
}
The
second resource bundle, shown next, is called SampleRB_de. It contains the German translation.
import java.util.*;
// German version.
public class SampleRB_de
extends ListResourceBundle { protected Object[][] getContents() {
Object[][] resources = new
Object[3][2];
resources[0][0] =
"title"; resources[0][1] = "Mein Programm";
resources[1][0] =
"StopText"; resources[1][1] = "Anschlag";
resources[2][0] =
"StartText"; resources[2][1] = "Anfang";
return resources;
}
}
The
following program demonstrates these two resource bundles by displaying the
string associated with each key for both the default (English) version and the
German version:
// Demonstrate a resource
bundle.
import java.util.*;
class LRBDemo {
public static void
main(String args[]) {
// Load the default bundle.
ResourceBundle rd = ResourceBundle.getBundle("SampleRB");
System.out.println("English
version: ");
System.out.println("String
for Title key : " +
rd.getString("title"));
System.out.println("String
for StopText key: " + rd.getString("StopText"));
System.out.println("String
for StartText key: " + rd.getString("StartText"));
// Load the German bundle.
rd =
ResourceBundle.getBundle("SampleRB", Locale.GERMAN);
System.out.println("\nGerman
version: "); System.out.println("String for Title key : " + rd.getString("title"));
System.out.println("String
for StopText key: " + rd.getString("StopText"));
System.out.println("String
for StartText key: " + rd.getString("StartText"));
}
}
The
output from the program is shown here:
English version:
String for Title key : My
Program
String for StopText key: Stop
String for StartText key:
Start
German version:
String for Title key : Mein
Programm
String for StopText key:
Anschlag
String for StartText key:
Anfang
Related Topics