Chapter: Java The Complete Reference : The Java Library : java.util : More Utility Classes
StringTokenizer - java.util
StringTokenizer
The
processing of text often consists of parsing a formatted input string. Parsing is the division of text into a
set of discrete parts, or tokens,
which in a certain sequence can convey a semantic meaning. The StringTokenizer class provides the
first step in this parsing process, often called the lexer (lexical analyzer) or scanner.
StringTokenizer implements the Enumeration interface. Therefore, given
an input string, you can enumerate the individual tokens contained in it using StringTokenizer.
To use StringTokenizer, you specify an input
string and a string that contains delimiters. Delimiters are characters that separate tokens. Each character in
the delimiters string is considered a
valid delimiter—for example, ",;:"
sets the delimiters to a comma, semicolon, and colon. The default set of
delimiters consists of the whitespace characters: space, tab, form feed,
newline, and carriage return.
The StringTokenizer constructors are shown
here:
StringTokenizer(String
str) StringTokenizer(String str, String delimiters)
StringTokenizer(String
str, String delimiters, boolean delimAsToken)
In all
versions, str is the string that will
be tokenized. In the first version, the default delimiters are used. In the
second and third versions, delimiters
is a string that specifies the delimiters. In the third version, if delimAsToken is true, then the delimiters are also returned as tokens when the
string is parsed. Otherwise, the delimiters are not returned. Delimiters are
not returned as tokens by the first two forms.
Once you
have created a StringTokenizer
object, the nextToken( ) method is
used to extract consecutive tokens. The hasMoreTokens(
) method returns true while
there are more tokens to be extracted. Since StringTokenizer implements Enumeration,
the hasMoreElements( ) and nextElement( ) methods are also
implemented, and they act the same as hasMoreTokens(
) and nextToken( ),
respectively. The StringTokenizer
methods are shown in Table 19-1.
Here is
an example that creates a StringTokenizer
to parse "key=value" pairs. Consecutive sets of "key=value"
pairs are separated by a semicolon.
// Demonstrate
StringTokenizer.
import
java.util.StringTokenizer;
class STDemo {
static String in =
"title=Java: The Complete Reference;" + "author=Schildt;" +
"publisher=McGraw-Hill;"
+ "copyright=2014";
public static void
main(String args[]) { StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(in,
"=;");
while(st.hasMoreTokens()) {
String key = st.nextToken(); String val = st.nextToken();
System.out.println(key +
"\t" + val);
}
}
}
The
output from this program is shown here:
title Java: The Complete
Reference author Schildt
publisher McGraw-Hill copyright
2014
Method :
Description
int
countTokens( ) : Using the current set of delimiters, the method determines the
number of tokens left to be parsed and returns the result.
boolean
hasMoreElements( ) : Returns true if one or more tokens remain in the string
and returns false if there are none.
boolean
hasMoreTokens( ) : Returns true if one or more tokens remain in the string and
returns false if there are none.
Object
nextElement( ) : Returns the next token as an Object.
String
nextToken( ) : Returns the next token as a String.
String
nextToken(String delimiters) : Returns the next token as a String and sets the
delimiters string to that specified by delimiters.
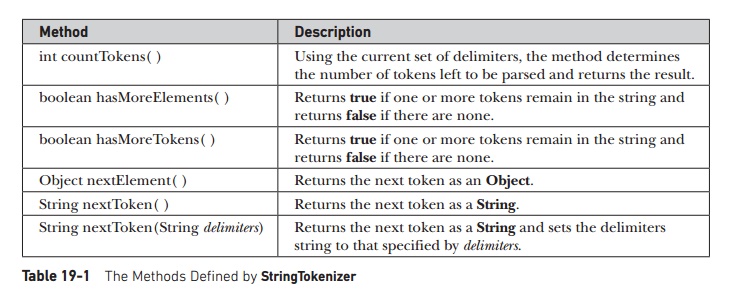
Table 19-1 The Methods Defined by StringTokenizer
Related Topics