Chapter: Java The Complete Reference : The Java Library : java.util : More Utility Classes
BitSet - java.util
BitSet
A BitSet class creates a special type of
array that holds bit values in the form of boolean
values. This array can increase in size as needed. This makes it similar to a
vector of bits. The BitSet
constructors are shown here:
BitSet(
) BitSet(int size)
The
first version creates a default object. The second version allows you to
specify its initial size (that is, the number of bits that it can hold). All
bits are initialized to false.
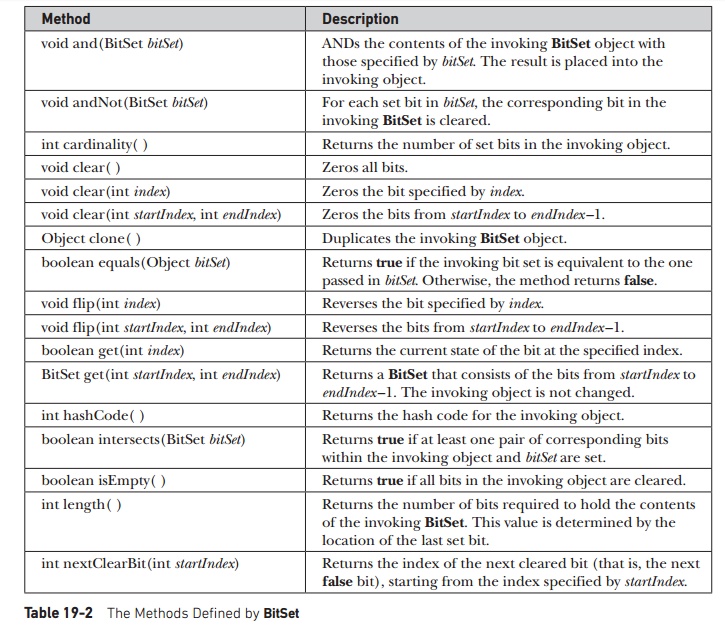
BitSet defines the methods listed in Table 19-2.
Method :
Description
void
and(BitSet bitSet) : ANDs the contents of the invoking BitSet object with those
specified by bitSet. The result is placed into the invoking object.
void
andNot(BitSet bitSet) : For each set bit in bitSet, the corresponding bit in
the invoking BitSet is cleared.
int
cardinality( ) : Returns the number of set bits in the invoking object.
void
clear( ) : Zeros all bits.
void
clear(int index) : Zeros the bit specified by index.
void
clear(int startIndex, int endIndex) : Zeros the bits from startIndex to
endIndex –1.
Object
clone( ) : Duplicates the invoking BitSet object.
boolean
equals(Object bitSet) : Returns true if the invoking bit set is equivalent to
the one passed in bitSet. Otherwise, the method returns false.
void
flip(int index) : Reverses the bit specified by index.
void
flip(int startIndex, int endIndex) : Reverses the bits from startIndex to
endIndex –1.
boolean
get(int index) : Returns the current state of the bit at the specified index.
BitSet
get(int startIndex, int endIndex) : Returns a BitSet that consists of the bits
from startIndex to endIndex –1. The invoking object is not changed.
int
hashCode( ) : Returns the hash code for the invoking object.
boolean
intersects(BitSet bitSet) : Returns true if at least one pair of corresponding
bits within the invoking object and bitSet are set.
boolean
isEmpty( ) : Returns true if all bits in the invoking object are cleared.
int
length( ) : Returns the number of bits required to hold the contents of the
invoking BitSet. This value is determined by the location of the last set bit.
int
nextClearBit(int startIndex) : Returns the index of the next cleared bit (that
is, the next false bit), starting from the index specified by startIndex.
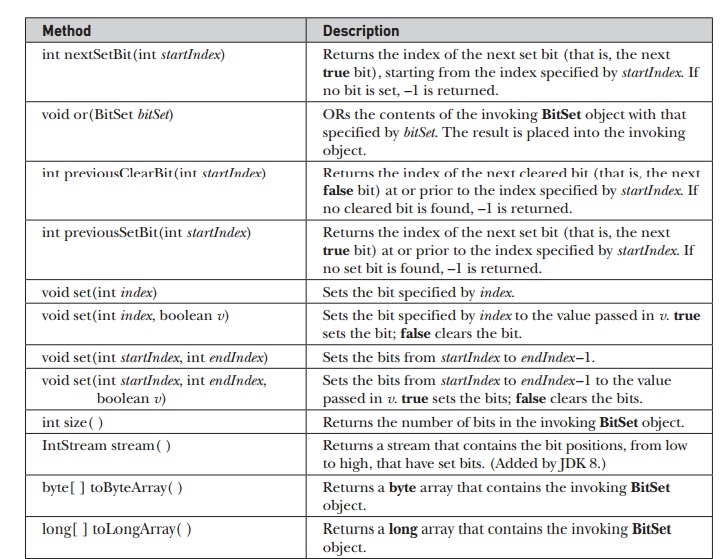
int
nextSetBit(int startIndex) : Returns the index of the next set bit (that is,
the next true bit), starting from the index specified by startIndex. If no bit
is set, –1 is returned.
void
or(BitSet bitSet) : ORs the contents of the invoking BitSet object with that
specified by bitSet. The result is placed into the invoking object.
int
previousClearBit(int startIndex) : Returns the index of the next cleared bit
(that is, the next false bit) at or prior to the index specified by startIndex.
If no cleared bit is found, –1 is returned.
int
previousSetBit(int startIndex) : Returns the index of the next set bit (that
is, the next true bit) at or prior to the index specified by startIndex. If no
set bit is found, –1 is returned.
void
set(int index) : Sets the bit specified by index.
void
set(int index, boolean v) : Sets the bit specified by index to the value passed
in v. true sets the bit; false clears the bit.
void
set(int startIndex, int endIndex) : Sets the bits from startIndex to
endIndex –1.
void
set(int startIndex, int endIndex, : Sets the bits from startIndex to
endIndex –1 to the value
boolean
v) : passed in v. true sets the bits; false clears the bits.
int
size( ) : : Returns the number of bits
in the invoking BitSet object.
IntStream
stream( ) : Returns a stream that contains the bit positions, from low to high,
that have set bits. (Added by JDK 8.)
byte[ ]
toByteArray( ) : Returns a byte array that contains the invoking BitSet object.
long[ ]
toLongArray( ) : Returns a long array that contains the invoking BitSet object.
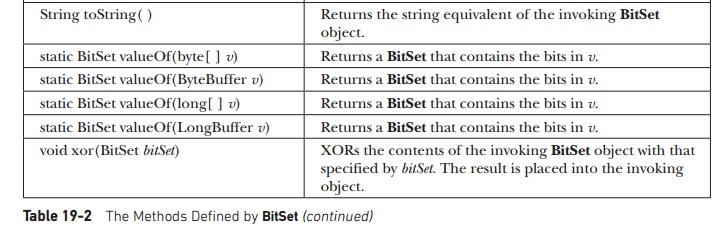
String
toString( ) : Returns the string equivalent of the invoking BitSet object.
static
BitSet valueOf(byte[ ] v) : Returns a BitSet that contains the bits in v.
static
BitSet valueOf(ByteBuffer v) : Returns a BitSet that contains the bits in v.
static
BitSet valueOf(long[ ] v) : Returns a BitSet that contains the bits in v.
static
BitSet valueOf(LongBuffer v) : Returns a BitSet that contains the bits in v.
void
xor(BitSet bitSet) : XORs the contents of the invoking BitSet object with that
specified by bitSet. The result is placed into the invoking object.
:
Table
19-2 The Methods Defined by BitSet :
Here is
an example that demonstrates BitSet:
// BitSet Demonstration.
import java.util.BitSet;
class BitSetDemo {
public static void
main(String args[]) { BitSet bits1 = new BitSet(16);
BitSet bits2 = new
BitSet(16);
// set some bits
for(int i=0; i<16; i++) {
if((i%2) == 0) bits1.set(i);
if((i%5) != 0) bits2.set(i);
}
System.out.println("Initial
pattern in bits1: ");
System.out.println(bits1);
System.out.println("\nInitial
pattern in bits2: "); System.out.println(bits2);
AND bits bits2.and(bits1);
System.out.println("\nbits2
AND bits1: ");
System.out.println(bits2);
OR bits
bits2.or(bits1);
System.out.println("\nbits2 OR bits1: "); System.out.println(bits2);
// XOR bits bits2.xor(bits1);
System.out.println("\nbits2
XOR bits1: ");
System.out.println(bits2);
}
}
The
output from this program is shown here. When toString( ) converts a BitSet
object to its string equivalent, each set bit is represented by its bit
position. Cleared bits are not shown.
Initial pattern in bits1: {0,
2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14}
Initial pattern in bits2:
{1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11,
12, 13, 14}
bits2 AND bits1:
{2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 14}
bits2 OR bits1:
{0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14}
bits2 XOR bits1: {}
Related Topics