Chapter: Java The Complete Reference : The Java Library : java.util : More Utility Classes
Calendar - java.util
Calendar
The
abstract Calendar class provides a
set of methods that allows you to convert a time in milliseconds to a number of
useful components. Some examples of the type of information that can be
provided are year, month, day, hour, minute, and second. It is intended that
subclasses of Calendar will provide
the specific functionality to interpret time information according to their own
rules. This is one aspect of the Java class library that enables you to write
programs that can operate in international environments. An example of such a
subclass is GregorianCalendar.
Calendar provides no public constructors. Calendar defines several protected
instance variables. areFieldsSet is a boolean that indicates if the time components have been set. fields is an array of ints that holds the components of the
time. isSet is a boolean array that indicates
if a specific time component has been set. time
is a long that holds the current
time for this object. isTimeSet is a
boolean that indicates if the
current time has been set.
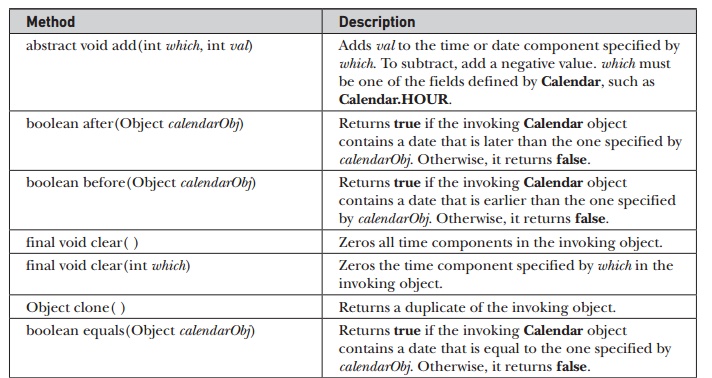
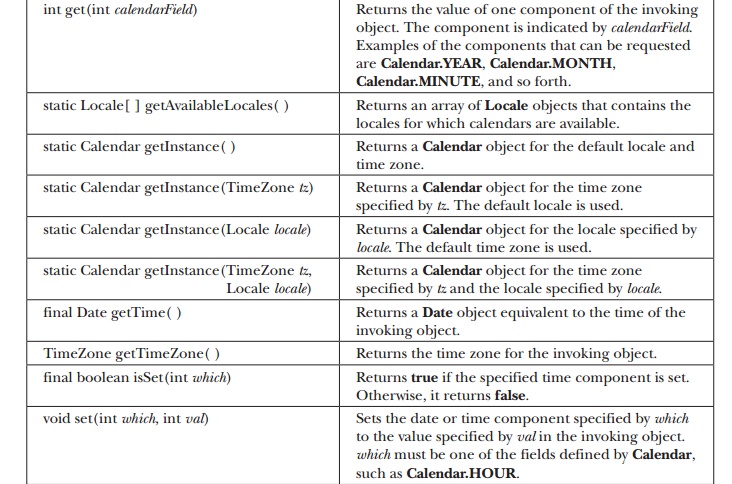
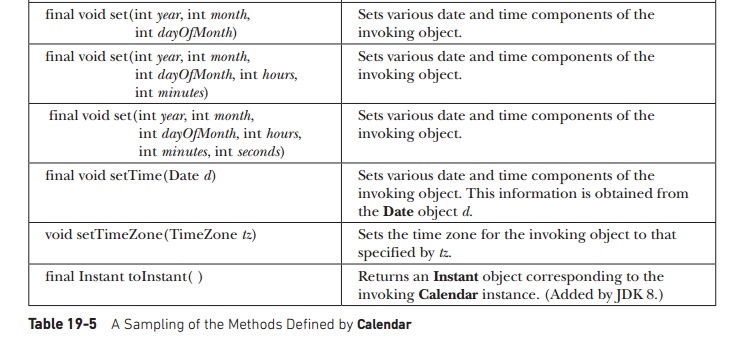
A
sampling of methods defined by Calendar
are shown in Table 19-5.
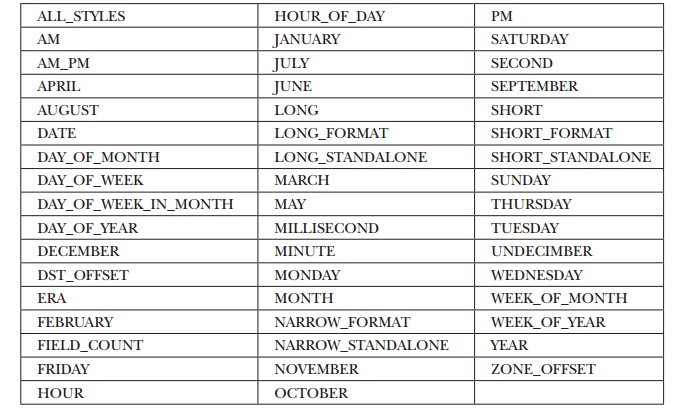
Calendar defines the following int constants, which are used when you get or set components of the calendar. (The ones
with the suffix FORMAT or STANDALONE were added by JDK 8.)
ALL_STYLES
AM
AM_PM
APRIL
AUGUST
DATE
DAY_OF_MONTH
DAY_OF_WEEK
DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_MONTH
DAY_OF_YEAR
DECEMBER
DST_OFFSET
ERA
FEBRUARY
FIELD_COUNT
FRIDAY
HOUR
HOUR_OF_DAY
JANUARY
JULY
JUNE
LONG
LONG_FORMAT
LONG_STANDALONE
MARCH
MAY
MILLISECOND
MINUTE
MONDAY
MONTH
NARROW_FORMAT
NARROW_STANDALONE
NOVEMBER
OCTOBER
PM
SATURDAY
SECOND
SEPTEMBER
SHORT
SHORT_FORMAT
SHORT_STANDALONE
SUNDAY
THURSDAY
TUESDAY
UNDECIMBER
WEDNESDAY
WEEK_OF_MONTH
WEEK_OF_YEAR
YEAR
ZONE_OFFSET
The
following program demonstrates several Calendar
methods:
// Demonstrate Calendar
import java.util.Calendar;
class CalendarDemo {
public static void
main(String args[]) {
String
months[] = {
"Jan", "Feb", "Mar", "Apr",
"May", "Jun", "Jul",
"Aug",
"Sep", "Oct", "Nov",
"Dec"};
Create a calendar initialized with the
current date and time in the default
locale and timezone.
Calendar calendar =
Calendar.getInstance();
// Display current time and
date information.
System.out.print("Date:
");
System.out.print(months[calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH)]);
System.out.print("
" + calendar.get(Calendar.DATE) + " ");
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR));
System.out.print("Time:
");
System.out.print(calendar.get(Calendar.HOUR)
+ ":");
System.out.print(calendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE)
+ ":");
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.SECOND));
// Set the time and date
information and display it.
calendar.set(Calendar.HOUR, 10);
calendar.set(Calendar.MINUTE,
29);
calendar.set(Calendar.SECOND,
22);
System.out.print("Updated time: ");
System.out.print(calendar.get(Calendar.HOUR)
+ ":");
System.out.print(calendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE)
+ ":");
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.SECOND));
}
}
Sample
output is shown here:
Date: Jan 1 2014
Time: 11:29:39
Updated time: 10:29:22
Related Topics