Chapter: Mechanical : Heat and Mass Transfer : Conduction
The General Heat Conduction Equation in Cartesian and Polar coordinates
The General Heat Conduction Equation in
Cartesian coordinates and Polar coordinates
Any
physical phenomenon is generally accompanied by a change in space and time of
its physical properties. The heat transfer by conduction in solids can only
take place when there is a variation of temperature, in both space and time.
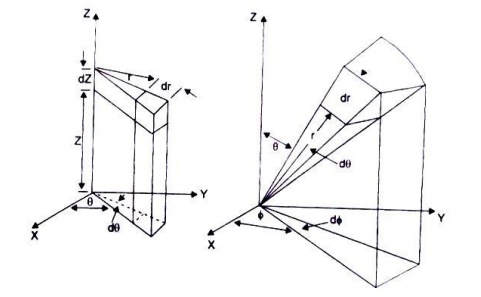
Let us consider a small volume of a solid element as shown in Fig. 1.2 The
dimensions are x-, Y-, and Z- coordinates.
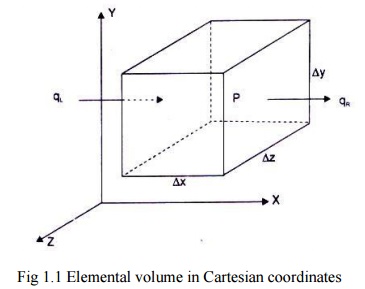
Fig
1.1 Elemental volume in Cartesian coordinates
First
we consider heat conduction the X-direction. Let T denote the temperature at
the point P (x, y, z) located at the geometric centre of the element. The
temperature gradient at the left hand face (x - ~x12) and at the right hand
face (x + x/2) , using the Taylor's series, can be written as:
¶T / x¶|L
=T/¶x ¶2T
/-x¶2.
x / 2¶+ higherD order terms.
¶T / x¶|R
=T/¶x ¶2T
/+x¶2.
x / 2¶ higherD order+
terms.
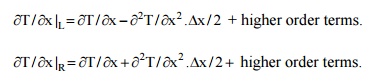
The
net rate at which heat is conducted out of the element 10 X-direction assuming
k as
constant
and neglecting the higher order terms,
Similarly
for Y- and Z-direction,
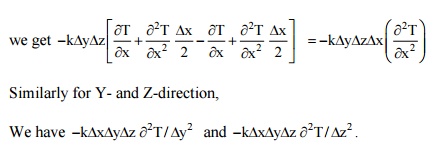
If
there is heat generation within the element as Q, per unit volume and the
internal energy of
the
element changes with time, by making an energy balance, we write
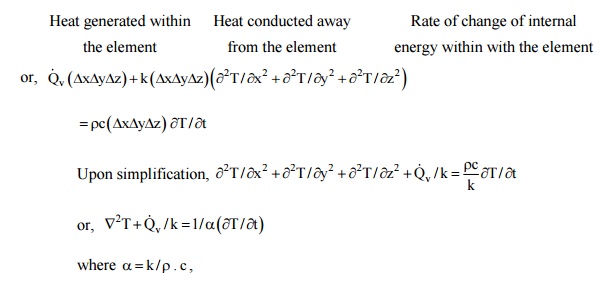
is called the thermal diffusivity and is seen to be a physical property of the
material of which the solid is composed.
The
Eq. (2.la) is the general heat conduction equation for an isotropic solid with
a constant
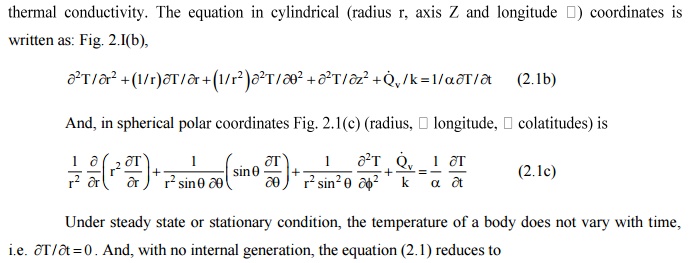
Under steady state or
stationary condition, the temperature of a body does not vary with time, i.e. ¶T / t¶
0=.And, with no internal generation,
the equation (2.1) reduces to
Del2T =0
It
should be noted that Fourier law can always be used to compute the rate of heat
transfer by conduction from the knowledge of temperature distribution even for
unsteady condition and with internal heat generation.
Related Topics