Definition, Formula, Solved Example Problems | Mensuration | Mathematics - Surface Area: Right Circular Cylinder | 10th Mathematics : UNIT 7 : Mensuration
Chapter: 10th Mathematics : UNIT 7 : Mensuration
Surface Area: Right Circular Cylinder
Surface Area
Surface area is the measurement of all exposed area of a solid
object.
Right Circular Cylinder
Observe the given figures in Fig.7.2 and identify the shape.

These objects resemble the shape of a cylinder.
Definition :
A right circular cylinder is a solid generated by the revolution
of a rectangle about one of its sides as axis.
If the axis is perpendicular to the radius then the cylinder is
called a right
circular cylinder. In the Fig.7.3, AB = h represent the height and
AD = r represent the radius of the cylinder.
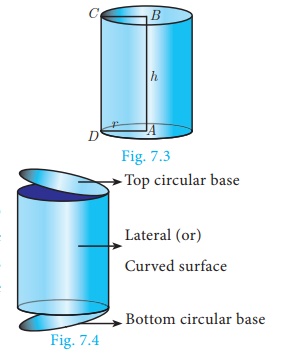
A solid cylinder is an object bounded by two circular plane
surfaces and a curved surface. The area between the two circular bases is
called its ‘Lateral Surface Area’ (L.S.A.) or ‘Curved Surface Area’ (C.S.A.).
Formation of a Right Circular Cylinder – Demonstration
(i) Take a rectangle sheet of a paper of length l and
breadth b.
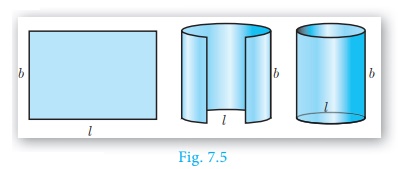
(ii) Revolve the paper about one of its sides, say b to
complete a full rotation (without overlapping).
(iii) The shape thus formed will be a right
circular cylinder whose circumference of the base is l and the
height is b.
Surface Area of a Right Circular Cylinder
(i) Curved surface area
Curved surface area (C.S.A.) of a right circular cylinder
= Area of the corresponding
rectangle
= l ×b
= 2πr ×h
(since, l is the circumference of the base, b is the height)[see
Fig. 7.5]
= 2πrh

C.S.A. of a right circular cylinder = 2πrh sq. units.
(ii) Total surface area
Total surface area refers to the sum of areas of the curved
surface area and the two circular regions at the top and bottom.
That is, total surface area (T.S.A.) of right circular cylinder
= C.S.A + Area of top circular region +Area of
bottom circular region.
= 2πrh + πr 2
+ πr 2 (Refer Fig.7.4)
= 2πrh + 2πr 2
= 2πr (h + r )

T.S.A. of a right circular cylinder = 2πr (h + r)
sq. units
Note
We always consider π = 22/7 , unless
otherwise stated.
The term ‘surface area’ refers to ‘total surface area’.
Example 7.1
A cylindrical drum has a height of 20 cm and base radius of 14 cm. Find its curved surface area and
the total surface area.
Solution
Given that, height of the cylinder h = 20 cm ; radius r =14 cm
Now, C.S.A. of the cylinder = 2πrh sq. units
C.S.A. of the cylinder = 2 × (22/7) × 14 ×20 = 2 ×22 × 2 ×20
= 1760 cm2
T.S.A. of the cylinder = 2πr (h+ r) sq. units
= 2 × (22/7) × 14 ×(20 +
14) = 2 × 22/7 × 14 ×34
= 2992 cm2
Therefore, C.S.A. = 1760 cm2 and T.S.A. = 2992 cm2
Example 7.2
The curved surface area of a right circular cylinder of height 14 cm is 88 cm2 . Find
the diameter of the cylinder.
Solution
Given that, C.S.A. of the cylinder =88 sq. cm
2πrh =88
2 × (22/7) × r ×14 =88 (given h=14 cm)
2r = (88×7) / (22×14) = 2
Therefore, diameter = 2 cm
Example 7.3
A garden roller whose length is 3 m long and whose diameter is 2.8 m is rolled to level a
garden. How much area will it cover in 8 revolutions?
Solution
Given that, diameter d = 2.8 m and height = 3 m
radius r = 1.4 m

Area covered in one revolution = curved surface area of the
cylinder
= 2πrh sq. units
= 2 × (22/7) × 1.4 ×3 = 26.4
Area covered in 1 revolution = 26.4 m2
Area covered in 8 revolutions = 8 ×26.4 = 211.2
Therefore, area covered is 211.2 m2
Thinking Corner
1. When ‘h’ coins each of radius ‘r’ units and
thickness 1 unit is stacked one upon the other, what would be the solid object
you get? Also find its C.S.A.
2. When the radius of a cylinder is double its height, find the
relation between its C.S.A. and base area.
3. Two circular cylinders are formed by rolling two rectangular
aluminum sheets each of dimensions 12 m length and 5 m breadth, one by rolling
along its length and the other along its width. Find the ratio of their curved
surface areas.
Related Topics