Chapter: Civil Surveying : GPS Surveying
Structure of The GPS Navigation Data
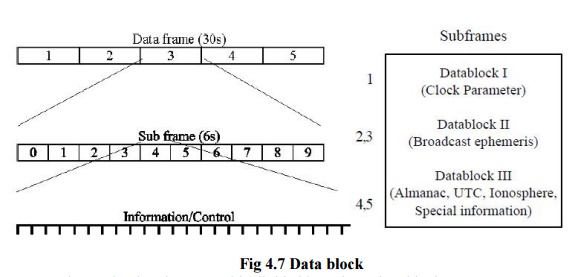
STRUCTURE OF THE GPS NAVIGATION DATA
Structure of GPS navigation data
(message) is shown in Fig. 7. The user has to decode the data signal to get
access to the navigation data. For on line navigation purposes, the internal processor
within the receiver does the decoding. Most of the manufacturers of GPS
receiver provide decoding software for post processing purposes. With a bit
rate of 50 bps and a cycle time of 30 seconds, the total information content of
a navigation data set is 1500 bits. The complete data frame is subdivided into
five subframes of six-second duration comprising 300 bits of information. Each
subframe contains the data words of 30 bits each. Six of these are control
bits. The first two words of each subframe are the Telemetry Work (TLM) and the
C/A-P-Code Hand over Work (HOW). The TLM work contains a synchronization
pattern, which facilitates the access to the navigation data. Since GPS is a
military navigation system of US, a limited access to the total system accuracy
is made available to the civilian users. The service available to the civilians
is called Standard Positioning System (SPS) while the service available to the
authorized users is called the Precise Positioning Service (PPS). Under current
policy the accuracy available to SPS users is 100m, 2D- RMS and for PPS users
it is 10 to 20 meters in 3D. Additional limitation viz. Anti-Spoofing (AS), and
Selective Availability (SA) was further imposed for civilian users. Under AS,
only authorized users will have the means to get access to the P-code. By
imposing SA condition, positional accuracy from Block-II satellite was randomly
offset for SPS users. Since May 1, 2000 according to declaration of US
President, SA is switched off for all users.
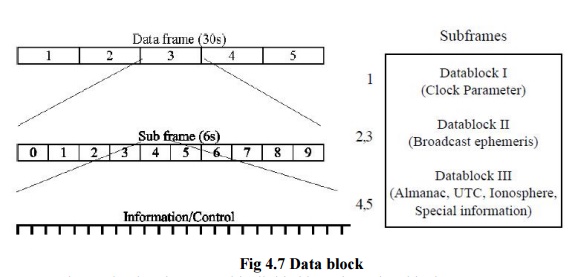
Fig 4.7
Data block
The
navigation data record is divided into three data blocks:
Data Block I appears in the first subframe and
contains the clock coefficient/bias.
Data Block II appears in the second and third
subframe and contains all necessary parameters for the computation of the
satellite coordinates.
Data Block III appears in the
fourth and fifth subframes and contains the almanac data with clock and
ephemeris parameter for all available satellite of the GPS
system. This data block includes also ionospheric correction
parameters and particular alphanumeric information for authorized users.
Unlike the first two blocks, the subframe four and
five are not repeated every 30 seconds.
International
Limitation of the System Accuracy
The GPS system time is defined by
the cesium oscillator at a selected monitor station. However, no clock
parameter are derived for this station. GPS time is indicated by a week number
and the number of seconds since the beginning of the current week. GPS time
thus varies between 0 at the beginning of a week to 6,04,800 at the end of the
week. The initial GPS epoch is January 5, 1980 at 0 hours Universal Time.
Hence, GPS week starts at Midnight (UT ) between Saturday and Sunday. The GPS
time is a continuous time scale and is defined by the main clock at the Master
Control Station (MCS). The leap seconds is UTC time scale and the drift in the
MCS clock indicate that GPS time and UTC are not identical. The difference is
continuously monitored by the control segment and is broadcast to the users in
the navigation message. Difference of about 7 seconds was observed in July,
1992.
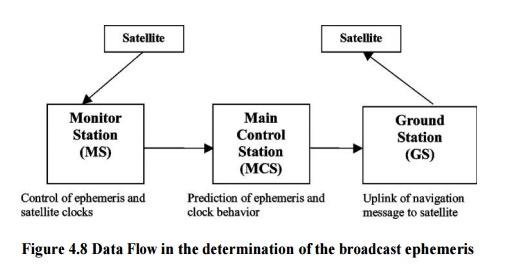
Figure
4.8 Data Flow in the determination of the broadcast ephemeris
GPS satellite is identified by
two different numbering schemes. Based on launch sequence, SVN (Space Vehicle
Number) or NAVSTAR number is allocated. PRN (Pseudo Random Noise) or SVID
(Space Vehicle Identification) number is related to orbit arrangement and the
particular PRN segment allocated to the individual satellite. Usually the GPS
receiver displays PRN number.
Related Topics