Chapter: Civil Surveying : GPS Surveying
Differential GPS
DIFFERENTIAL GPS
Most DGPS techniques use a GPS receiver at a geodetic control
site whose position is known. The receiver collects positioning information and
calculates a position fix, which is then compared to the known co-ordinates.
The difference between the known position and the acquired position of the
control location is the positioning error.
Because the other GPS receivers in the area are
assumed to be operating under similar conditions, it is assumed that the
position fixes acquired by other receivers in the area (remote units) are
subject to the same error, and that the correction computed for the control
position should therefore be accurate for those receivers. The correction is
communicated to the remote units by an operator at the control site with radio
or cellular equipment. In post-processed differential, all units collect data
for off-site processing; no corrections are determined in the field. The
process of correcting the position error with differential mode is shown in the
Figure .
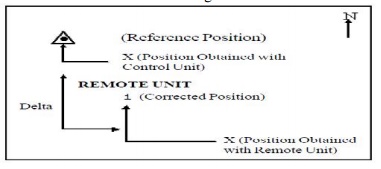
The difference between the known
position and acquired position at the control point is the DELTA correction.
DELTA, which is always expressed in meters, is parallel to the surface of the
earth. When expressed in local co- ordinate system, DELTA uses North-South axis
(y) and an East-West axis (x) in 2D operation; an additional vertical axis (z)
that is perpendicular to the y and x is used in 3D operation for altitude.
Related Topics