Chapter: Civil Surveying : GPS Surveying
GPS Surveying: Space Segment
GPS Surveying
SPACE
SEGMENT
Space segment will consist 21 GPS
satellites with an addition of 3 active spares. These satellites are placed in
almost six circular orbits with an inclination of 55 degree. Orbital height of
these satellites is about 20,200 km corresponding to about 26,600 km from the
semi major axis. Orbital period is exactly 12 hours of sidereal time and this
provides repeated satellite configuration every day advanced by four minutes
with respect to universal time.
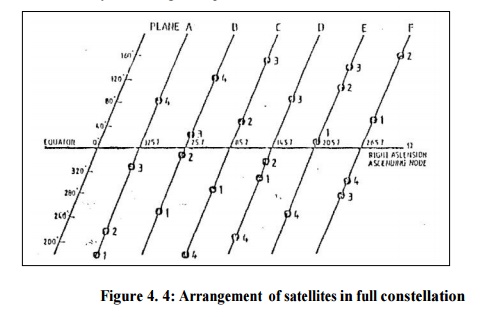
Final arrangement of 21
satellites constellation known as 'Primary
satellite constellation' is given in Fig. 4. There are
six orbital planes A to F with a separation of 60 degrees at right ascension
(crossing at equator). The position of a satellite within a particular orbit
plane can be identified by argument of latitude or mean anomaly M for a given
epoch.
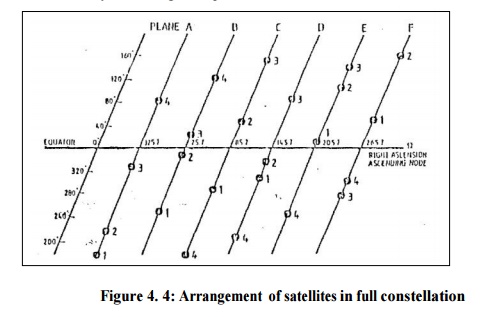
Figure 4.
4: Arrangement of satellites in full constellation
GPS satellites are broadly
divided into three blocks: Block-I satellite pertains to development stage,
Block II represents production satellite and Block IIR are replenishment/spare
satellite.
Under Block-I, NAVSTAR 1 to 11
satellites were launched before 1978 to 1985 in two orbital planes of 63-degree
inclination. Design life of these prototype test satellites was only five years
but the operational period has been exceeded in most of the cases.
The first Block-II production
satellite was launched in February 1989 using channel Douglas Delta 2 booster
rocket. A total of 28 Block-II satellites are planned to support 21+3 satellite
configuration. Block-II satellites have a designed lifetime of 5-7 years.
To sustain the GPS facility, the
development of follow-up satellites under Block-II R has started. Twenty
replenishment satellites will replace the current block-II satellite as and
when necessary. These GPS satellites under Block-IR have additional ability to
measure distances between satellites and will also compute ephemeris on board
for real time information gives a schematic view of Block-II satellite.
Electrical power is generated through two solar panels covering a surface area
of 7.2 square meter each. However, additional battery backup is provided to
provide energy when the satellite moves into earth's shadow
region. Each satellite weighs 845kg and has a propulsion system for positional
stabilization and orbit maneuvers.
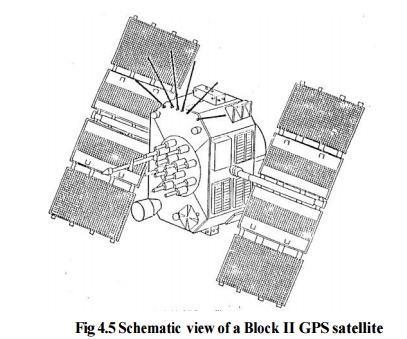
Fig 4.5
Schematic view of a Block II GPS satellite
GPS satellites have a very high performance frequency standard
with an accuracy of
between 1X10-12 to
1X10-13 and are thus capable of creating precise time base. Block-I
satellites were partly equipped with only quartz oscillators but Block-II
satellites have two cesium frequency standards and two rubidium frequency
standards. Using fundamental frequency of 10.23 MHz, two carrier frequencies
are generated to transmit signal codes.
Related Topics