Chapter: Mobile Computing
Structure of Mobile Computing Application
STRUCTURE OF MOBILE COMPUTING
APPLICATION
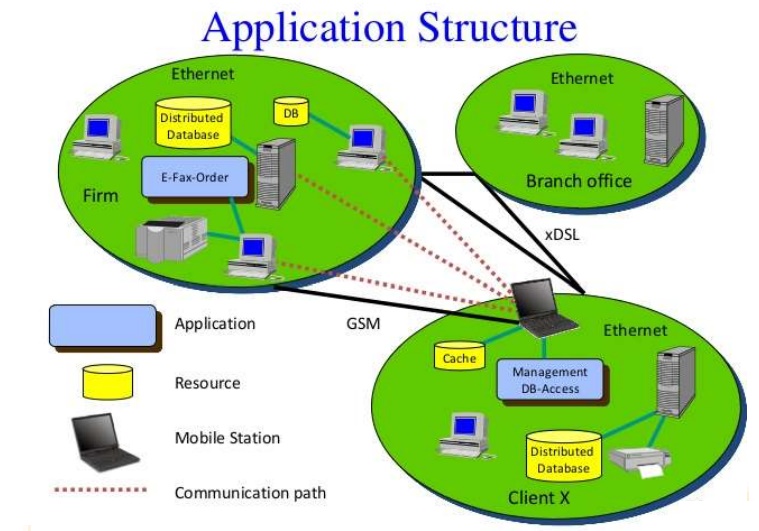
Programming languages are used for mobile system
software. Operating system functions to run the software components onto the
hardware. Middleware components deployment. Layered structure arrangement of
mobile computing components is used. Protocols and layers are used for
transmission and reception.
Programming Languages
The
following are the programming languages used for Mobile Computing applications
are:
·
Java - J2SE.
·
J2ME (Java2 Micro edition)
·
JavaCard (Java for smart card)
·
The Java enterprise edition (J2EE) used for web and
enterprise server based applications of mobile services
·
C and C++
·
Visual C++
·
Visual Basic
Operating System
Symbian
OS, Window CE, Mac OS are the operating systems used in Mobile computing
applications. It offers the user to run an application without considering the
hardware specifications and functionalities. It provides functions which are
used for scheduling the multiple tasks in a system.
It
provides the functions required for the synchronization of multiple tasks in
the system. It uses multiple threads synchronization and priority allocation.
Management functions (such as creation, activation, deletion, suspension, and
delay) are used for tasks and memory. It provides Interfaces for communication
between software components at the application layer, middleware layers, and
hardware devices.
It
facilitates the execution of software components on diversified hardware. It
provides Configurable libraries for the GUI (graphic user interface) in the
device. It provides
User
application‘s GUIs, VUI (voice user interface) components, and phone API. It
provides the device drivers for the keyboard, display, USB, and other devices.
Middleware
Software
components that link the application components with the network-distributed
components. It is used to discover the nearby device such as Bluetooth. It is
used to discover the nearby hot spot for achieving device synchronization with
the server or an enterprise server. It is used for retrieving data (which may
be in Oracle or DB2) from a network database. It is used for service discovery
at network. It is used for adaptation of the application to the platform and
service availability.
Architecture of Mobile Computing Applications
Client/server
architecture (and its variants) is often adopted for this kind of applications.
However we have to take into consideration some specific aspects related to the
mobile devices (clients), and their connectivity with servers.
Clients
There are
many mobile device types, including RIM devices, cellular telephones, PDAs,
Tablet, PCs, and Laptop PCs. These mobile devices can typically operate as thin
clients or fat clients, or they can be developed so that they can host web
pages
Thin Clients
Thin
clients have no custom application code and completely rely on the server for
their functionality. They do not depend as heavily on the mobile device‘s
operating system or the mobile device type as fat clients. Thin clients
typically use widely available web and Wireless Application Protocol (WAP)
browsers to display the application content pages.
Fat Clients
Fat clients typically have one to three layers of
application code on them and can operate independently from a server for some
period of time. Typically, fat clients are most useful in situations where
communication between a client and server cannot be guaranteed.
For
example, a fat client application may be able to accept user input and store
data in a local database until connectivity with the server is re-established
and the data can be moved to the server.
This allows a user to continue working even if
he/she is out of contact with the server. Fat clients depend heavily on the
operating system and mobile device type and the code can be difficult to
release and distribute. Fat clients can be implemented using one, two, or three
layers of application code. However, if you only use one layer it is extremely
difficult to isolate the individual areas of functionality and reuse and
distribute the code over multiple device types.
Related Topics