Chapter: Biochemistry: Immunology
Structure and Types of Antigens
Structure and Types of Antigens
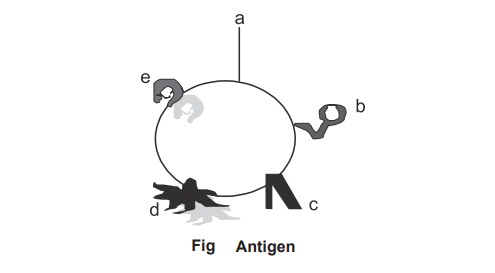
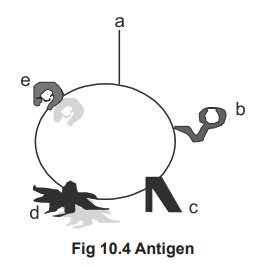
An antigen molecule may contain a number of
similar group or different antigenic determinant. The figure 10.4 shows that a
cell which contains different groups of molecules over the surface. However
only the group a andd has been selected for antigen
processing. Hence a andd are antigenic determinant. Normally
antigens are multi determinant.
Types of antigen
Antigen possesses several unique molecular
structures which can induce an immune response. Most antigens are proteins,
nucleoproteins, lipoproteins,
glycoproteins, or large polysaccharides with a
molecular weight greater than 10,000. To become an antigen the molecule must be
relatively having a higher molecular weight. Large antigenic molecule posses
many antigenic determinant per molecule. However the low-molecular-weight
substance that can combine with an antibody but cannot induce the formation of
antibodies are called as haptens.
They can also initiate antibody response when they are combined covalently with
a carrier molecule. Since antigens
stimulate the immune response they are other wise called as immunogens.
Related Topics