Chapter: Biochemistry: Immunology
Cell mediated immunity
Cell mediated immunity
T cells are responsible for cell-mediated immunity. T cells are initially formed in the bone
marrow and get its maturation and differentiation in the thymusgland. After maturation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid organ. T cells
areclassified according to their functions and cell-surface marker called CDs (clusters ofdifferentiation). They are
functionally classified as T helper, T suppressor, T memoryand T killer cells. T cells are associated with certain
types of allergic reactions called Delayed
hypersensitivity and also in transplanted organ rejection.
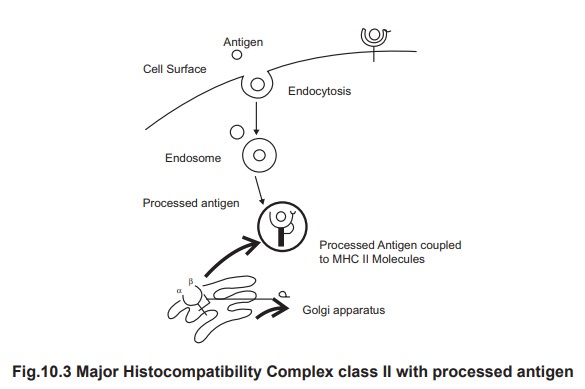
The Major
Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) are unique to each individual and indicate
self-molecules and always these
molecules are given as reference when ever an antigen is presented and this
helps the immune system to differentiate the self from non-self. (fig. 3) Helper T (TH) cells (also
known as CD4 cells) activate B cells
to produce antibodies against T-dependent antigens (usually protein in
composition). TH cells recognize and bind to an antigen in association with an MHC II (Fig. 3) on the surface of an
antigen presenting cells (APC) and
the APC cell secrete the cytokineIL-1 and induce the THcell
to secrete the cytokine IL-2. Only THcells
that have been stimulated by an antigen have
receptors for IL-2 and thus these THcells are specificfor only that
stimulatory antigen. Production of IL-2 and other cytokines by these TH
cells stimulates the cell-mediated (e.g., TC cells) and humoral (B
cells- Plasma cell) immune responses. In Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome
(AIDS),the Human Immuno deficiency virus (HIV) affect the T helper cells. Suppressor (TS) cells appear
to regulate the immune response once the antibody formation reached the
adequate levels. Cytotoxic T cells (CD8) identify the viral infected cells and
inject the molecule called Perforin to lyse the viral infected cells. Some of
the activated T cells become Tmemory
cells.
Role of lymphokines
Lymphokines are the cytokines secreted by the
lymphocytes and these are small molecules released due to a stimulus and help
to send the signal between cells. The term interleukin (IL) is also often
referring to the cytokine produced by leukocytes. There is considerable overlap
between the actions of the individual lymphokines, so that many of the above
effects are shared between TNFa, IL-2 to IL-12. In addition, these
proinflammatory cytokines activate the immune system, mobilizing neutrophils
from bone marrow, causing dendritic cells to migrate to lymph nodes, and also
initiating changes in adipocyte and muscle metabolism and also responsible for
inducing fever.
Related Topics