Chapter: Biochemistry: Immunology
Antibody Structure
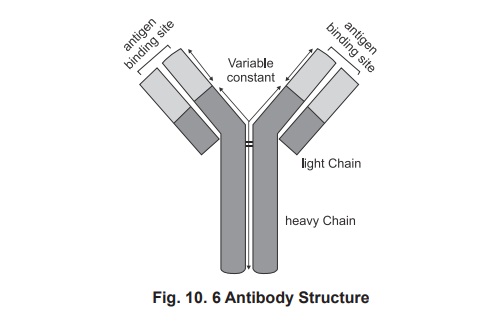
Antibody Structure
A single antibody unit is ‘Y’ shaped molecule which is chemically a glycoprotein forms the gamma globulin in plasma (Fig. 10.6).
Most antibody monomers consist of four polypeptide chains. Two are heavy chains and two are light chains. There is a constant region, which is specific for
a particular classof antibodies. For IgM the heavy chain is m, for IgG it is g, for IgA is a, for IgD it
is d, and for IgE it is e. The light chain may either be k (or) l (kappa or
lamda). The chains are folded into discrete regions called domains. There are 2
domain in the light chain and 4 to 5 domain in the heavy chains. In the
constant region the free end forms the FC portion. There is a
variable region present in the heavy and light chain and called as variable (V) region, where antigen binding
occurs. Hence in a given antibody molecule two binding sites are available.
Related Topics