Chapter: Biochemistry: Immunology
Antibodies
Antibodies
Antibodies found in the serum and other body
fluids of vertebrates that react specifically with the Ag. Antibody belongs to
a family of globular protein called Immunoglobulin. Antibody are Gamma
globulins, in normal immune response antibodies are heterogeneous. It provides
defense against extra cellular antigen.
Antibody has two main functions,
1.
Bind
specifically to foreign or non self molecules.
2.
Recruit
other cells and molecule to destroy the pathogen (effectors function or
Biological activity)
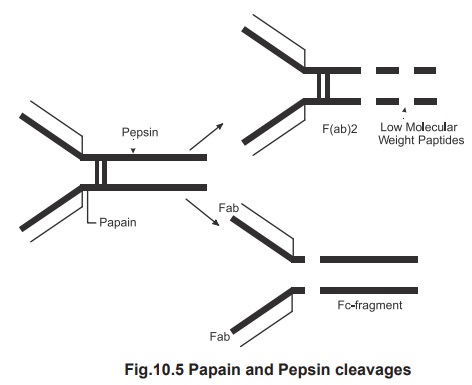
To understand the function of various ends in
the antibody molecule the more abundant IgG molecule when subjected to papain
and pepsin cleavages, as shown (Fig.10.5), the papain cleavage yields 2
monovalent Fab molecule which combine with the antigen (Fragment antigen
binding) and one Fc part which can be the fragment crystalisable. When the same
IgG molecule subjected to pepsin cleavage it resulted with a divalent antigen
binding Fab part and fragments of Fc portion. This is because the papain
cleaves between the heavy chain and the hinge region .The pepsin cleaves after
the disulfide bridge. This enzymatic digestion also indicates that the two
disulfide bond hold the chains together. However the Fc portion is essential
for biological activity. Fc region
can attach to a host cell or complement or helps to cross the placenta.
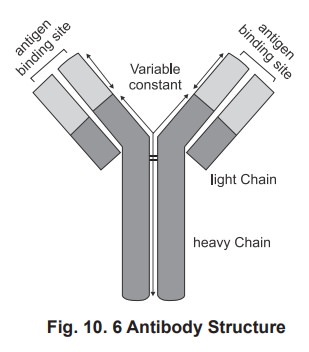
1. Antibody Structure
A single antibody unit is ‘Y’ shaped molecule which is chemically a glycoprotein forms the gamma globulin in plasma (Fig. 10.6).
Most antibody monomers consist of four polypeptide chains. Two are heavy chains and two are light chains. There is a constant region, which is specific for
a particular classof antibodies. For IgM the heavy chain is m, for IgG it is g, for IgA is a, for IgD it
is d, and for IgE it is e. The light chain may either be k (or) l (kappa or
lamda). The chains are folded into discrete regions called domains. There are 2
domain in the light chain and 4 to 5 domain in the heavy chains. In the
constant region the free end forms the FC portion. There is a
variable region present in the heavy and light chain and called as variable (V) region, where antigen binding
occurs. Hence in a given antibody molecule two binding sites are available.
2. Types of immunoglobulins
An antibody
or immunoglobulin (Ig) is
glycoprotein produced by B cells, which is capable of combining specifically
with the antigen, which induces it. Antibodies are divided into five major
classes, IgM, IgG, IgA, IgD and IgE, based on their heavy chain constant region
structure. An antibody has at least two identical antigen-bindingsites and it is the valence of an antibody.
3. Immunoglobulin and their functions
IgG
has two light chains
either kappa or lambda and two heavy chain ofgtypeand consists of four
subclasses IgG1, IgG2, IgG3 and IgG4. It is predominant class of immunoglobulin
and account for approximately 80% in human serum. IgG produced particularly
during the secondary immune response. IgG stimulates phagocytic cells,
activates the complement system, binds neutrophils, and can neutralize toxins.
Most importantly, it is the only antibody that can cross the placenta and
confer immunity on the foetus.
IgA
has two light chains
either kappa or lambda and two heavy chain ofatypeand consist of two subclasses
IgA1 and IgA2, constitutes only 13% of the antibody in human serum, but
predominant class of antibody in extravascular secretions. The IgA present in secretions
(tears, saliva, nasal secretions and mammary gland secretions) is secretory
IgA. It is found to produce immunity against tapeworms and present in the
colostrums protects the baby from intestinal pathogens.
IgM
has two light chains
either kappa or lambda and two heavy chain ofmtypeconstitutes 8% of the
antibody in human serum, it is the largest of the immunoglobulins often
referred as the macroglobulin because it has more than five binding sites for
antigen. It is the first antibody to appear in the primary immune response
therefore an useful indicator of recent infection. Most of the natural
antibodies like ABO blood grouping (anti-A anti-B) are of the IgM class and
important in the initial activation of B-cells, macrophages, and activate the complement
system.
IgD
has two light chains
either kappa or lambda and two heavy chain ofdtypeconstitute less than 1% of
the antibody in human serum. Plays a role in activating and suppressing
lymphocyte activity and found large quantities in the cell walls of many
B-cells. IgD has a single binding site.
IgE
is a reaginic antibody, has
two light chains either kappa or lambda andtwo heavy chain of e type constitute
less than 0.003% of the antibody in human serum. Mediator in allergic
responses. Most importantly activates histamine secreting cells. Also appears
to play a role in parasitic infection and mediates type one hypersensitivity.
Related Topics