Chapter: Biochemistry: Immunology
Antigens
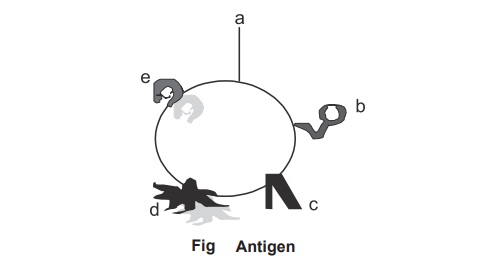
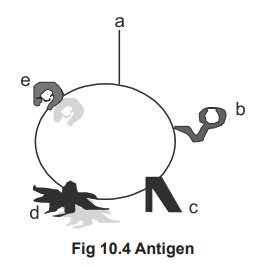
Antigens
An antigen
is a foreign substance, which is
recognized by the immune system. Antigens can be defined as a substance that
can combine specifically to the components of immune response such as
lymphocytes and antibodies. An immunogen is any substance that has the ability
to evoke B or T or both B and T mediated immune reactions. Whole antigen cannot
combine with the antibody as antibodies are formed against specific regions on
the surface of an antigen called antigenic
determinantor epitopes.
1. Structure and Types of Antigens
An antigen molecule may contain a number of
similar group or different antigenic determinant. The figure 10.4 shows that a
cell which contains different groups of molecules over the surface. However
only the group a andd has been selected for antigen
processing. Hence a andd are antigenic determinant. Normally
antigens are multi determinant.
Types of antigen
Antigen possesses several unique molecular
structures which can induce an immune response. Most antigens are proteins,
nucleoproteins, lipoproteins,
glycoproteins, or large polysaccharides with a
molecular weight greater than 10,000. To become an antigen the molecule must be
relatively having a higher molecular weight. Large antigenic molecule posses
many antigenic determinant per molecule. However the low-molecular-weight
substance that can combine with an antibody but cannot induce the formation of
antibodies are called as haptens.
They can also initiate antibody response when they are combined covalently with
a carrier molecule. Since antigens
stimulate the immune response they are other wise called as immunogens.
2. Factors influencing the antigenicity of antigens
Antigen must be a foreign substance as more
foreign the substance, the more immunogenic in nature. However the following
factors can also influence it,
1.
The
antigenic response which is indicated by the quantum of antibody formed in
response to antigenic stimulation varies depending on the dosage of antigenadministered, route of administration and use of adjuvant etc.
2.
Molecular weight of the antigen affect the antigenicity as low
molecular antigenscan only combine with the antibody (hapten).
3.
Very
low molecular weight substance cannot act as an antigen. Because of this the
virus which has the very low molecular weight proteins escapes the immune
response.
4.
Very
large molecular antigen directly induces the B cell differentiation with out
the involvement of T Cells.
5.
Degradability is essential as in the antigen presenting cells
process the antigenby degrading them and processed peptide antigen along with
the MHC II molecule presented to the T cells and such antigens are called T dependent antigen.
6.
Antigen
induced antibody response can be suppressed by administrating the antibody
passively either prior to or shortly after administration of antigen (This is
utilized for the treatment of Rh antigen induced antibody in the mother leading
to Erythroblastosis fetalis).
Related Topics