Chapter: Biochemistry: Immunology
Antigen antibody reactions
Antigen antibody reactions
The interaction of an antigen determinant and
antibody molecule is called immune complex or antigen - antibody complex.
Various factors influencing antigen-antibody complex. Specificity antibody to
combine with only one type of antigen, Binding site of antigen and antibody (
epitope and paratope), Binding forces of antigen and antibody – closeness
between antigen and antibody and intermolecular forces, Affinity (attraction of
Ag- Ab binding ) and Avidity (combining capacity of heterogenous antibodies
with multivalent antigen).
The first interaction of an antigenic
determinant (epitope) with its corresponding antigen binding site on an
antibody is called a primary antigen- antibody reaction. The primary
antigen-antibody reactions are rapid reaction, not dependent on electrolytes
and not visible. If the primary antigen- antibody reaction is followed by the
aggregation of antigen antibody complexes into macroscopically visible clumps
is called the secondary antigen-antibody reaction and this aggregation phase
may take hours to day to reach maximum. The two visible reactions are called
precipitation and agglutination.
1. Precipitation
Precipitation is the combination of soluble
antigen with specific antibody, which leads to the formation of an insoluble
aggregation. Immune precipitation occurs when antigen and antibody combine in
solution and form a visible aggregate. Precipitation reaction is quantifiable.
The variation in the ratio of antibody- antigen leads to different levels of
lattice formation, and thereby to different amounts of precipitate. This
phenomenon, called the prozone phenomenon were antibody may excess, zone of
equivalence of antigen- antibody or antigen may excess. Factors affect
precipitation are temperature, pH, salt concentration and reaction volume.
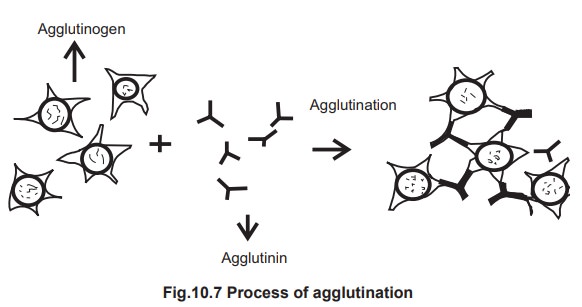
2. Agglutination
The clumping, or agglutination, of particulate
antigens by specific antibodies. Clumping results in the formation of a lattice
in which antigen and antibody are cross linked. Agglutination methods are
qualitative or semi quantitative at best and its reaction can be used in many
applications as it posses a high degree of sensitivity. Agglutination reactions
can be classified as either direct or indirect. In the direct agglutination
reaction, the antigenic determinant is a normal constituent of the particle
surface. In the indirect agglutination a molecule is ordinarily soluble is
attached to a particle and rendered insoluble.
Related Topics