Chapter: Mechanical and Electrical : Power Plant Engineering : Power Plants and Boilers
Steam Power Plants
STEAM POWER P LANTS
A thermal power station is a
power plant in which the prime mo ver is steam driven. Water is heated, turns
into ste am and spins a steam turbine which drives an electrical generator.
After it passes through the tur bine, the steam is condensed in a condenser an
d recycled to where it was heated; this is known as a Rankine cycle. The
greatest variation in t he design of thermal power stations is due to the
different fuel sources. Some prefer to use the term energy center
because such facilities convertt forms of heat energy into electricity. Some t
hermal power plants also deliver heat energy for industrial purposes, for district
heating, or for d esalination of water as well as delivering electric al power.
A large proportion of CO2 is prod uced by the worlds fossil fired thermal power
pla nts; efforts to reduce these outputs are various and widespread.
LAYOUT OF
STEAM POW ER PLANT:
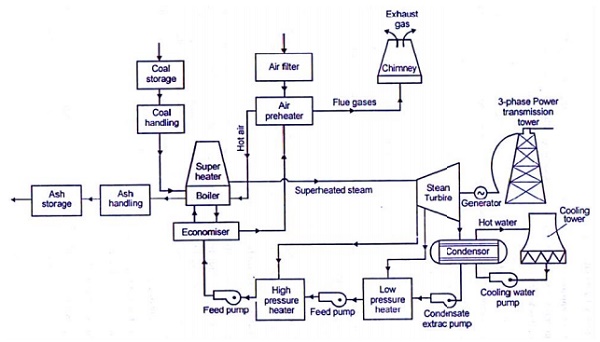
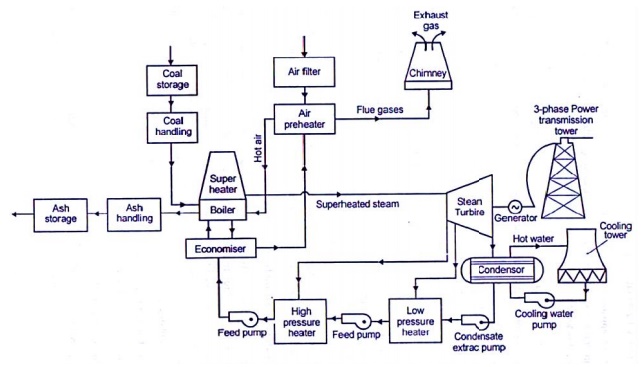
The four main circuits one wo uld come across in any thermal
power plant layout are
- Coal and
Ash Circuit
- Air and
Gas Circuit
- Feed
Water and Steam Circu it
Cooling
Water Circuit
Coal and Ash Circuit
Coal and Ash circuit in a thermal
power plant layout mainly takes care of feeding the boiler with coal from the
storage for combustion. The ash that is generated during combustion is
collected at the back of the boiler and removed to the ash storage by scrap
conveyors. The combustion in the Coal and Ash circuit is controlled by
regulating the speed and the quality of coal entering the grate and the damper
openings.
Air and Gas Circuit
Air from the atmosphere is
directed into the furnace through the air preheated by the action of a forced
draught fan or induced draught fan. The dust from the air is removed before it
enters the combustion chamber of the thermal power plant layout. The exhaust
gases from the combustion heat the air, which goes through a heat exchanger and
is finally let off into the environment.
Feed Water and Steam Circuit
The steam produced in the boiler
is supplied to the turbines to generate power. The steam that is expelled by
the prime mover in the thermal power plant layout is then condensed in a
condenser for re-use in the boiler. The condensed water is forced through a
pump into the feed water heaters where it is heated using the steam from
different points in the turbine. To make up for the lost steam and water while
passing through the various components of the thermal power plant layout, feed
water is supplied through external sources. Feed water is purified in a
purifying plant to reduce the dissolve salts that could scale the boiler tubes.
Cooling Water Circuit
The quantity of cooling water
required to cool the steam in a thermal power plant layout is significantly
high and hence it is supplied from a natural water source like a lake or a
river. After passing through screens that remove particles that can plug the
condenser tubes in a thermal power plant layout, it is passed through the
condenser where the steam is condensed. The water is finally discharged back
into the water source after cooling. Cooling water circuit can also be a closed
system where the cooled water is sent through cooling towers for re-use in the
power plant. The cooling water circulation in the condenser of a thermal power
plant layout helps in maintaining a low pressure in the condenser all
throughout.
All these
circuits are integrated to form a thermal power plant layout that generates
electricity to meet our needs.
Advantages
Ø Generation
of power is continuous.
Ø Initial
cost low compared to hydel plant.
Ø Less
space required.
Ø This can
be located near the load centre so that the transmission losses are reduced.
Ø It can
respond to rapidly changing loads.
Disadvantages
Ø Long time
required for installation.
Ø Transportation
and handling of fuels major difficulty.
Ø Efficiency
of plant is less.
Ø Power
generation cost is high compared to hydel power plant.
Ø Maintenance
cost is high.
Related Topics