Chapter: Mechanical and Electrical : Power Plant Engineering : Power Plants and Boilers
Fluidised Bed Combustion (FBC)
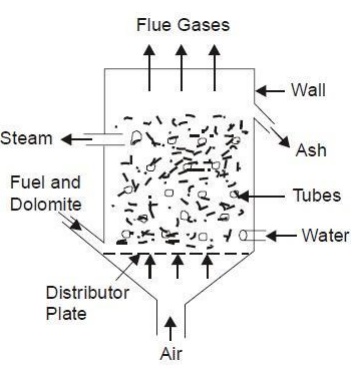
FLUIDISED
BED COMBUSTION (FBC)
Fluidised Bed
combustion system can burn any fuel including low grade coals (even containing
70% ash), oil, gas or municipal waste. Improved desulphurisation and low NOX
emission are its main characteristics. The fuel and inert material dolomite are
fed on a distribution plate and air is supplied from the bottom of distribution
plate. The air is supplied at high velocity so that solid feed material remains
in suspension condition during burning.
The heat produced is used to heat water flowing through the tube
and convert water into
steam. During burning SO2 formed is absorbed by
the dolomite and thus prevents its escape
with the exhaust gases. The molten slag is
tapped from the top surface of the bed. The bed
temperature is nearly 800-9000C which
is ideal for sulphur retention addition of limestone or
dolomite to the bed brings down SO2 emission
level to about 15% of that in conventional firing
methods.
Various advantages of FBC system are as follows:
1. FBC system can use any type of low grade fuel including
municipal wastes and therefore is a cheaper method of power generation.
2. It is easier to control the amount of SO2 and NOX, formed during burning. Low emission of SO2 and NOX will help in controlling the undesirable effects of SO2 and NOX. During combustion. SO2 emission is nearly 15% of that in conventional firing methods.
3. There is a saving of about 10% in operating cost and 15% in the
capital cost of the power plant.
4. The size of coal used has pronounced effect on the operation and
performance of FBC system. The particle size preferred is 6 to 13 mm but even
50 mm size coal can also be used in this system.
The major
portion of the coal available in India is of low quality, high ash content and
low calorific value. The traditional grate fuel firing systems have got
limitations and are techno-economically unviable to meet the challenges of
future. Fluidized bed combustion has emerged as a viable alternative and has
significant advantages over conventional firing system and offers multiple
benefits – compact boiler design, fuel flexibility,
higher combustion efficiency and reduced emission of noxious pollutants such as
SOx and NOx.
Related Topics