Chapter: Mechanical and Electrical : Power Plant Engineering : Power Plants and Boilers
Gas Turbine Power Plants
GAS TURBINE POWER PLANTS
A gas turbine, also called a
combustion turbine, is a type of internal combustion engine. It has an upstream
rotating compressor coupled to a downstream turbine, and a combustion chamber
in-between.
Energy is
added to the gas stream in the combustor, where fuel is mixed with air and
ignited. In the high pressure environment of the combustor, combustion of the
fuel increases the temperature. The products of the combustion are forced into
the turbine section. There, the high velocity and volume of the gas flow is
directed through a nozzle over the turbine's blades, spinning the turbine which
powers the compressor and, for some turbines, drives their mechanical output.
The energy given up to the turbine comes from the reduction in the temperature
and pressure of the exhaust gas.
LAYOUT OF GAS TURBINE POWER PLANT
The gas turbine power plants
which are used in electric power industry are classified into two groups as per
the cycle of operation.
(1) Open cycle
gas turbine.
(2) Closed
cycle gas turbine.
Open
cycle gas turbine
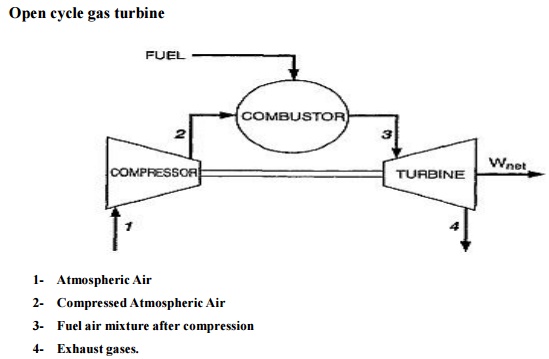
1- Atmospheric Air
2- Compressed Atmospheric Air
3- Fuel air mixture after compression
4- Exhaust gases.
The heated gases coming out of
combustion chamber are then passed to the turbine where it expands doing
mechanical work. Part of the power developed by the turbine is utilized in
driving the compressor and other accessories and remaining is used for power
generation.
Since ambient air enters into the
compressor and gases coming out of turbine are exhausted into the atmosphere,
the working medium must be replaced continuously. This type of cycle is known
as open cycle gas turbine plant and is mainly used in majority of gas turbine
power plants as it has many inherent advantages.
Advantages
1. Warm-up
time is very less.
2. Low
weight and size.
3. Almost
any hydrocarbon fuels can be used.
4. Open
cycle plants occupy comparatively little space.
6. Very
economical when compared to other plants.
7. Independent
of separate cooling medium.
Disadvantages
1. The part
load efficiency of the open cycle plant decreases rapidly as the considerable
percentage of power developed by the turbine is used to drive the compressor.
2. The
system is sensitive to the component efficiency; particularly that of
compressor.
3. The open
cycle plant is sensitive to changes in the atmospheric air temperature,
pressure and humidity.
3. The
open-cycle gas turbine plant has high air rate compared to the other cycles.
4. It is
essential that the dust should be prevented from entering into the compressor.
5. The
deposition of the carbon and ash on the turbine blades is not at all desirable
as it also reduces the efficiency of the turbine.
Closed
cycle gas turbine
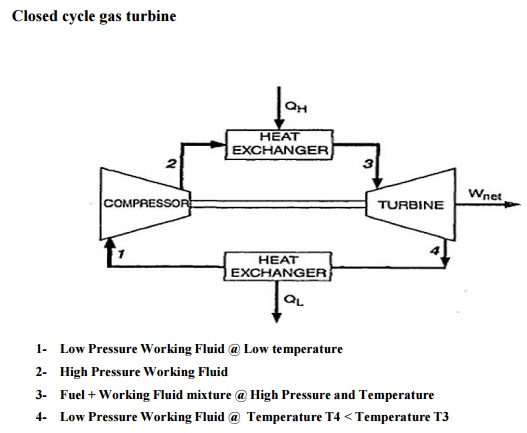
1- Low Pressure Working Fluid @ Low temperature
2- High Pressure Working Fluid
3- Fuel + Working Fluid mixture @ High Pressure
and Temperature 4- Low Pressure Working Fluid @ Temperature T4 <
Temperature T3
In closed cycle gas turbine
plant, the working fluid (air or any other suitable gas) coming out from
compressor is heated in a heater by an external source at constant pressure.
The high
temperature and high-pressure air coming out from the external heater is passed
through the gas turbine. The fluid coming out from the turbine is cooled to its
original temperature in the cooler using external cooling source before passing
to the compressor.
The working fluid is continuously used in the system without
its change of phase and the
required heat is given to the working fluid in the heat
exchanger.
Advantages
1.The closed cycle plant is not
sensitive to changes in the atmospheric air temperature, pressure and humidity.
2. The
closed cycle avoids erosion of the turbine blades due to the contaminated gases
and fouling of compressor blades due to dust.
3. The need
for filtration of the incoming air which is a severe problem in open cycle
plant is completely eliminated.
4. Load
variation is usually obtained by varying the absolute pressure and mass flow of
the circulating medium, while the pressure ratio, the temperatures and the air
velocities remain almost constant.
5. The
density of the working medium can be maintained high by increasing internal
pressure range, therefore, the compressor and turbine are smaller for their rated
output. The high density of the working fluid further increases the heat
transfer properties in the heat exchanger.
6. As
indirect heating is used in closed cycle plant, the inferior oil or solid fuel
can be used in the furnace and these fuels can be used more economically
because these are available in abundance.
8. The
maintenance cost is low and reliability is high due to longer useful life.
Disadvantages
1. The
system is dependent on external means as considerable quantity of cooling water
is required in the pre-cooler.
2. Higher
internal pressures involve complicated design of all components and high
quality material is required which increases the cost of the plant.
3. The
response to the load variations is poor compared to the open-cycle plant.
4. It requires
very big heat-exchangers as the heating of workings fluid is done indirectly.
Related Topics