Chapter: Mechanical and Electrical : Power Plant Engineering : Neclear Power Plants
Nuclear Reactor
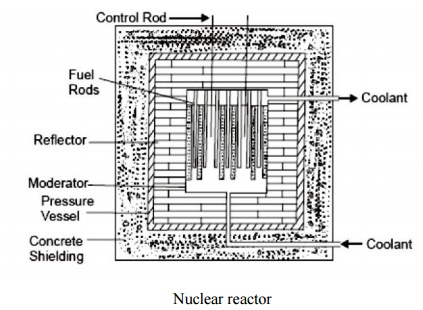
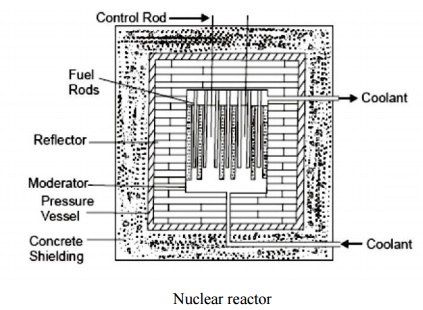
NUCLEAR REACTOR
A nuclear reactor is an apparatus in which heat is produced due to nuclear fission chain reaction. Fig. shows the various parts of reactor, which are as follows:
1. Nuclear Fuel
2. Moderator
3. Control Rods
4. Reflector
5. Reactors Vessel
6. Biological Shielding
7. Coolant.
1. Nuclear Fuel
Fuel of a nuclear reactor should be fissionable material which can be defined as an element or isotope whose nuclei can be caused to undergo nuclear fission by nuclear bombardment and to produce a fission chain reaction. It can be one or all of the following U233, U235 and Pu239.
Natural uranium found in earth crust contains three isotopes namely U234, U235 and U238 and their average percentage is as follows:
U238 - 99.3%
U235 - 0.7%
U234 - Trace
2. Moderator
In the chain reaction the neutrons produced are fast moving neutrons. These fast moving neutrons are far less effective in causing the fission of U235 and try to escape from the reactor. To improve the utilization of these neutrons their speed is reduced. It is done by colliding them with the nuclei of other material which is lighter, does not capture the neutrons but scatters them. Each such collision causes loss of energy, and the speed of the fast moving neutrons is reduced. Such material is called Moderator. The slow neutrons (Thermal Neutrons) so produced are easily captured by the nuclear fuel and the chain reaction proceeds smoothly. Graphite, heavy water and beryllium are generally used as moderator
3. Control Rods
The Control and operation of a nuclear reactor is quite different from a fossil fuelled (coal or oil fired) furnace. The energy produced in the reactor due to fission of nuclear fuel during chain reaction is so much that if it is not controlled properly the entire core and surrounding structure may melt and radioactive fission products may come out of the reactor thus making it uninhabitable. This implies that we should have some means to control the power of reactor. This is done by means of control rods.
Control rods in the cylindrical or sheet form are made of boron or cadmium. These rods can be moved in and out of the holes in the reactor core assembly. Their insertion absorbs more neutrons and damps down the reaction and their withdrawal absorbs less neutrons. Thus power of reaction is controlled by shifting control rods which may be done manually or automatically.
4.Reflector
The neutrons produced during the fission process will be partly absorbed by the fuel rods, moderator, coolant or structural material etc. Neutrons left unabsorbed will try to leave the reactor core never to return to it and will be lost. Such losses should be minimized. It is done by surrounding the reactor core by a material called reflector which will send the neutrons back into the core. The returned neutrons can then cause more fission and improve the neutrons economy of' the reactor.
Generally the reflector is made up of graphite and beryllium.
5. Reactor Vessel
It is a. strong walled container housing the cure of the power reactor. It contains moderator, reflector, thermal shielding and control rods.
6. Biological Shielding
Shielding the radioactive zones in the reactor roan possible radiation hazard is essential
to protect, the operating men from the harmful effects. During fission of nuclear fuel, alpha particles, beta particles, deadly gamma rays and neutrons are produced. Out of these gamma rays are of main significance. A protection must be provided against them. Thick layers of lead or concrete are provided round the reactor for stopping the gamma rays. Thick layers of metals or plastics are sufficient to stop the alpha and beta particles.
7. Coolant
Coolant flows through and around the reactor core. It is used to transfer the large
amount of heat produced in the reactor due to fission of the nuclear fuel during chain reaction. The coolant either transfers its heat to another medium or if the coolant used is water it takes up the heat and gets converted into steam in the reactor which is directly sent to the turbine.
Related Topics