Chapter: Mechanical and Electrical : Power Plant Engineering : Neclear Power Plants
Main components of nuclear power plants
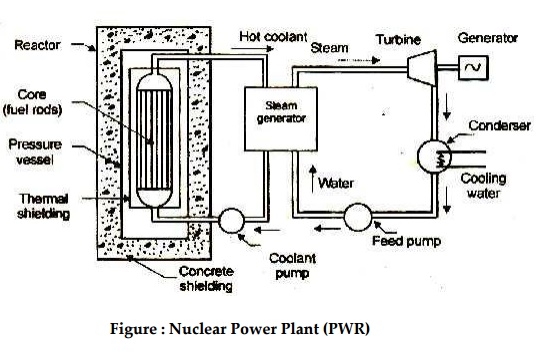
Main components of nuclear power plants:
i) Moderators
In any
chain reaction, the neutrons produced are fast moving neutrons. These are less effective
in causing fission of U235 and they try to escape from the reactor.
It is thus implicit that speed of these neutrons must be reduced if their
effectiveness is carrying out fission is to be increased. This is done by
making these neutrons collide with lighter nuclei of other materials, which
does not absorb these neutrons but simply scatter them. Each collision causes
loss of energy and thus the speed of neutrons is reduced. Such a material is
called a ‘Moderator’.The neutrons thus slowed down are easily captured by the
fuel element at the chain reaction proceeds slowly.
ii)
Reflectors
Some of the neutrons produced during fission will be
partly absorbed by the fuel elements, moderator, coolant and other materials.
The remaining neutrons will try to escape from the
reactor and will be lost. Such losses are minimized by
surrounding (lining) the reactor core with a material called a reflector which
will reflect the neutrons back to the core. They improve the neutron economy.
Economy: Graphite, Beryllium.
iii)
Shielding
During Nuclear fission ¥, b, gparticles and neutrons are also
produced. They are harmful to human life. Therefore it is necessary to shield
the reactor with thick layers of lead, or concrete to protect both the
operating personnel as well as environment from radiation hazards.
iv)
Cladding
In order to prevent the contamination of the coolant by
fission products, the fuel element is covered with a protective coating. This
is known as cladding.
Control rods are used to control the reaction to prevent
it from becoming violent. They control the reaction by absorbing neutrons.
These rods are made of boron or cadmium. Whenever the reaction needs to be
stopped, the rods are fully inserted and placed against their seats and when
the reaction is to be started the rods are pulled out.
v)
Coolant
The main purpose of the coolant in the reactor is to
transfer the heat produced inside the reactor. The same heat carried by the
coolant is used in the heat exchanger for further utilization in the power
generation.
Some of the desirable properties of
good coolant are listed below
1.
It
must not absorb the neutrons.
2.
It
must have high chemical and radiation stability
3.
It
must be non-corrosive.
4.
It
must have high boiling point (if liquid) and low melting point (if solid)
5.
It
must be non-oxidising and non-toxic.
The
above-mentioned properties are essential to keep the reactor core in safe
condition as well as for the better functioning of the content.
6. It
must also have high density, low viscosity, high conductivity and high specific
heat. These properties are essential for better heat transfer and low pumping
power.
The water, heavy water, gas (He, CO2), a metal in liquid
form (Na) and an organic liquid are used as coolants.
The coolant not only carries large amounts of heat from
the core but also keeps the fuel assemblies at a safe temperature to avoid
their melting and destruction.
vi)
Nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor may be regarded as a substitute for the
boiler fire box of a steam power plant. Heat is produced in the reactor due to
nuclear fission of the fuel U235 The heat liberated in the reactor
is taken up by the coolant circulating through the core. Hot coolant leaves the
reactor at top and flows into the steam generator (boiler).
Radiation
hazards and Shieldings
The
reactor is a source of intense radioactivity. These radiations are very harmful
to human life. It requires strong control to ensure that this radioactivity is
not released into the atmosphere to avoid atmospheric pollution. A thick
concrete shielding and a pressure vessel are provided to prevent the escape of
these radiations to atmosphere
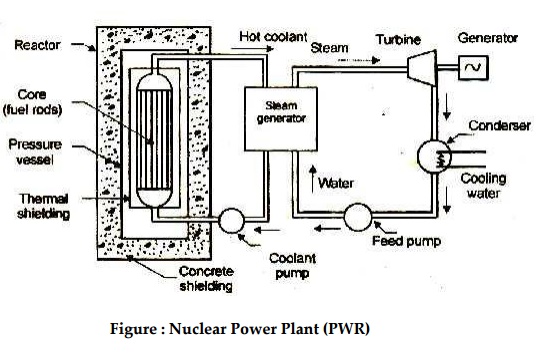
Figure : Nuclear Power Plant (PWR)
vii)
Steam generator
The steam generator is fed with feed water which is converted
into steam by the heat of the hot coolant. The purpose of the coolant is to
transfer the heat generated in the reactor core and use it for steam
generation. Ordinary water or heavy water is a common coolant.
viii)
Turbine
The steam produced in the steam generator is passed to the
turbine and work is done by the expansion of steam in the turbine.
ix)
Coolant pump and Feed pump
The steam from the turbine flows to the condenser where
cooling water is circulated. Coolant pump and feed pump are provided to
maintain the flow of coolant and feed water respectively.
Advantages
of nuclear power plant
1.
It
can be easily adopted where water and coal resources are not available.
2.
The
nuclear power plant requires very small quantity of fuel. Hence fuel transportation
cost is less.
3.
Space
requirement is less compared to other power plants of equal capacity.
4.
It
is not affected by adverse weather conditions.
5.
Fuel
storage facilities are not needed as in the case of the thermal power plant.
6.
Nuclear
power plants will converse the fossils fuels (coal, petroleum) for other energy
needs.
7.
Number
of workmen required at nuclear plant is far less than thermal plant.
8.
It
does not require large quantity of water.
Disadvantages
1.
Radioactive
wastes, if not disposed of carefully, have adverse effect on the health of
workmen and the population surrounding the plant.
2.
It
is not suitable for varying load condition.
3.
It
requires well-trained personnel.
4.
It
requires high initial cost compared to hydro or thermal power plants.
Related Topics