Uses, Origin and Area of cultivation, Botanical name - Spices and Condiments | 12th Botany : Chapter 10 : Economically Useful Plants and Entrepreneurial Botany
Chapter: 12th Botany : Chapter 10 : Economically Useful Plants and Entrepreneurial Botany
Spices and Condiments
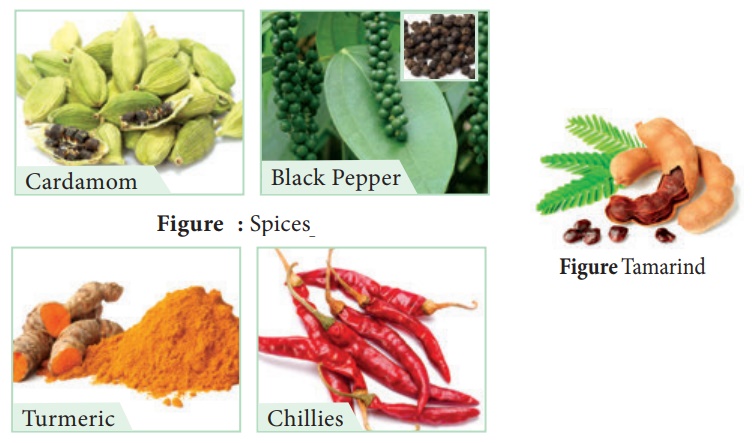

Spices and Condiments
“Aroma attracts everyone”
History:
Spices were used extensively throughout the world for several
thousands of years. Records of use of garlic and onion dates back 2500 years.
Majority of the spices are native to Mediterranean region, India
and South East Asian countries. Spices, especially pepper triggered the search
for sea route to India and paved way for the exploratory voyages by Spanish and
Portuguese.
Spices are accessory foods mainly used for flavouring during food
preparation to improve their palatability. Spices are aromatic plant products
and are characterized by sweet or bitter taste. Spices are added in minimal
quantities during the cooking process. For example black pepper.
Condiments, on the other hand, are flavouring substances having a
sharp taste and are usually added to food after cooking. For example, curry
leaves.
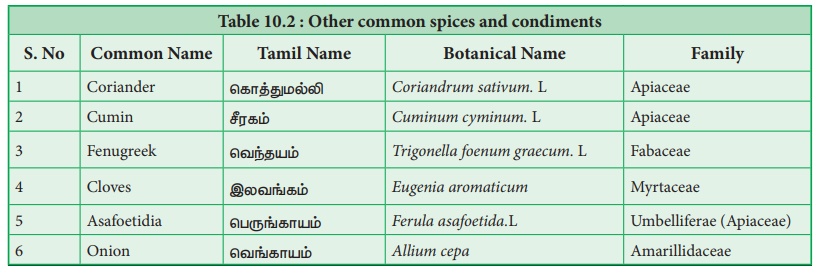
The following spices and condiment are discussed in detail.
1. Spices
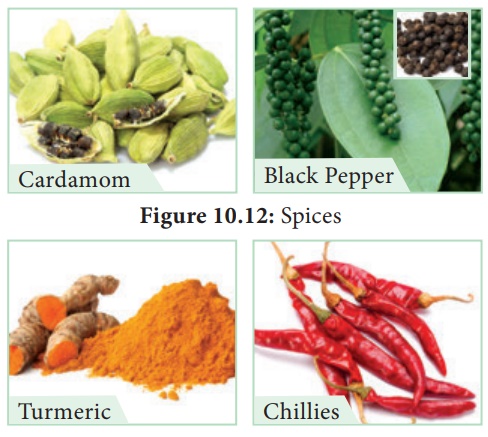
Cardamom
Botanical name : Elettaria cardamomum
Family : Zingiberaceae
Origin and Area of cultivation: It is indigenous to Southern India and
Sri Lanka. Cardamom is called as “Queen of Spices”. In India it is one of the
main cash crops cultivated in the Western Ghats, and North Eastern India
Uses
The seeds have a pleasing aroma and a characteristic warm, slightly pungent taste. It is used for flavouring confectionaries, bakery products and beverages. The seeds are used in the preparation of curry powder, pickles and cakes. Medicinally, it is employed as a stimulant and carminative. It is also chewed as a mouth freshener.
Black Pepper
Botanical name : Piper nigrum
Family : Piperaceae
Origin and Area of cultivation:
It is indigenous to Western Ghats of
India. Pepper is one of the most important Indian spices referred to as the
“King of Spices” and also termed as “Black Gold of India”. Kerala, Karnataka
and Tamil Nadu are the top producers in India.
The characteristic pungency of the pepper is due to the presence
of alkaloid Piperine. There are two types of pepper available in the market
namely black and white pepper.
Uses
It is used for flavouring in the preparation of sauces, soups,
curry powder and pickles. It is used in medicine as an aromatic stimulant for
enhancing salivary and gastric secretions and also as a stomachic. Pepper also
enhances the bio-absorption of medicines.
Turmeric
Botanical name : Curcuma longa
Family : Zingiberaceae
Origin and Area of cultivation:
It is indigenous to Southern Asia India is the largest producer, consumer and exporter of turmeric. Erode in Tamil Nadu is the World’s largest wholesale turmeric market.
Uses
Turmeric is one of the most important and ancient Indian spices
and used traditionally over thousands of years for culinary, cosmetic, dyeing
and for medicinal purposes. It is an important constituent of curry powders.
Turmeric is used as a colouring agent in pharmacy, confectionery and food
industry. Rice coloured with turmeric (yellow) is considered sacred and
auspicious which is used in ceremonies. It is also used for dyeing leather,
fibre, paper and toys.
Curcumin extracted from turmeric is responsible for the yellow
colour. Curcumin is a very good anti-oxidant which may help fight various kinds
of cancer. It has anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic, anti-bacterial, anti-fungal
and anti-viral activities. It stops platelets from clotting in arteries, which
leads to heart attack.

Chillies / Red Pepper
Botanical name : Capsicum annuum, c.frutescens.
Family : Solanaceae
Origin and Area of cultivation:
Capsicum is native to South America and
is popularly known as chillies or red pepper in English. India is leading
producer and exporter. C. annuum and C. frutescens are important
cultivated species of chillies.
Uses
The fruits of C.annuum are less pungent than the fruits of C.frutescens.
C.annum includes large, sweet bell peppers. Long fruit cultivars of this
species are commercially known as ‘Cayenne pepper’ which are crushed, powdered
and used as condiment. Chillies are used in manufacture of sauces, curry
powders and preparation of pickles. Capsaicin is an active component of
chillies. It has pain relieving properties and used in pain relieving balms.
Chillies are a good source of Vitamin C, A and E.
2. Condiment
Tamarind
Botanical name :Tamarindus indica
Family : Fabaceae-Caesalpinioideae
Origin and Area of cultivation:
Tamarind is native of tropical African region and was introduced into India several thousand years Figure 10.13 : Tamarind before. It is cultivated in India, Myanmar, south asian countries and several African and Central American countries.
Tamarind has long been used in Africa and in Southern Asia. The
name tamarindus is of Arabian origin, which means “dates of India”. (tamar –
dates; Indus – India).
Uses
It is used in flavouring sauces in the United States and Mexico.
In India, the fruit pulp is major ingredients for many culinary preparations.
Sweet tamarinds are sold as table fruits in India imported from Thailand and
Malaysia.

Related Topics