Economically Useful Plants and Entrepreneurial Botany - Answer the following questions (Pure Science Group) | 12th Botany : Chapter 10 : Economically Useful Plants and Entrepreneurial Botany
Chapter: 12th Botany : Chapter 10 : Economically Useful Plants and Entrepreneurial Botany
Answer the following questions (Pure Science Group)
Economically Useful Plants and Entrepreneurial Botany
Answer the following questions (Pure Science Group)
22. Write the cosmetic uses of
Aloe.
Answer: (i) ‘Aloin’ (a mixture of glucosides) and its gel are used as
skin tonic.
(ii) It has a cooling effect and moisturizing characteristics
and hence used in preparation of creams, lotions, shampoos, shaving creams,
after shave lotions and allied products.
(iii) It is used in gerontological applications for rejuvenation
of aging skin.
(iv) Products prepared from aloe leaves have multiple properties
such as emollient, antibacterial, antioxidant, antifungal and antiseptic.
(v) Aloe vera gel is used in skin care cosmetics.
23. What is pseudo cereal? Give
an example.
Answer: (i) The term
pseudo-cereal is used to describe foods that are prepared and eaten as a whole
grain, but are botanical outliers from grasses.
(ii) Example : quinoa - seed from the Chenopodium
quinoa plant.
(iii) It is a gluten-free, whole-grain carbohydrate, as well as
a whole protein.
24. What are cucurbits? Why it is
considered as an important summer vegetable?
Answer: The cucurbits are the vining plants of the family
Cucurbitaceae, which include cucumbers, squash, pumpkins, melons and gourds.
Origin and Area of Cultivation:
The cucumber is an
important summer vegetable in all parts of India.
Uses:
(i) Depending on the species immature or mature fruit are
consumed as fresh or cooked vegetables.
(ii) The vegetable can be stored for a long time after harvest
and is thus considered to be a summer vegetable.
25. Which fruit is rich in
potassium? Mention its economic importance.
Answer: (i) The banana fruit is loaded with potassium and essential
vitamins, which can be eaten raw or cooked (deep fried, dehydrated, baked or
steamed).
(ii) Fruit can be processed into flour and can be fermented for
the production of beverages such as banana juice, beer, vinegar and vine.
(iii) Tamil Nadu is the world’s No. 1 banana producer.
(iv) Major cultivars of banana are Chevazhai, Nentheran,
Karpooravalli, Poovan and Peyan.
26. Discuss which wood is better
for making furniture.
Answer: Teak
Botanical name : Tectona grandis
(i) It is one of best timbers of the world.
(ii) The heartwood is golden yellow to golden brown when freshly
sawn, turning darker when exposed to light.
(iii) Known for its durability as it is immune to the attack of
termites and fungi.
(iv) The wood does not split or crack and is a carpenter
friendly wood.
Rose wood
Botanical name: Dalbergia latifolia
Rose wood is native to
India.
(i) Indian rosewood has yellowish sapwood and dull brown to
almost purple coloured heartwood.
(ii) The wood is characterised by fragrant, heavy, narrowly
interlocked grained and medium coarse textured. It is a durable and heavy wood
and is suitable for under water use.
(iii) Wood is used for making furniture, army wagons, temple
chariots, cabinets, railway sleepers, musical instruments, hammer handles, shoe
heels and tobacco pipes.
Furniture is made
using teak wood / rose wood.
27. A person got irritation while
applying chemical dye. What would be your suggestion for alternative?
Answer: An orange dye ‘Henna’ is obtained from the leaves and
young shoots of Lawsonia inermis. The
principal colouring matter of leaves ‘lacosone” is harmless and causes no
irritation to the skin. This dye has long been used to dye skin, hair and
finger nails. It is used for colouring leather, for the tails of horses and in
hair-dyes.
28. Name the humors that are
responsible for the health of human beings.
Answer: Three humors namely Vatam, Pittam and Kapam are responsible for the health of human beings and any disturbance in the equilibrium of these humors result in ill health.
29. Give definitions for organic
farming?
Answer: Organic farming is an alternative agricultural system in
which plants/crops are cultivated in natural ways by using biological inputs to
maintain soil fertility and ecological balance thereby minimizing pollution and
wastage.
30. Define bonsai?
Answer: Bonsai is a Japanese art form using miniature trees grown
in containers that mimic the shape and scale of full size trees.
31. What is terrarium?
Answer: A terrarium is a collection of small plants growing in a
transparent, sealed container. Terrariums are easy to make, low maintenance
gardens, and it can survie indefinitely with minimal water.
32. Which is called as the “King
of Bitters”? Mention their medicinal importance.
Answer: Nilavembu
Botanical name: Andrographis
paniculata
Family: Acanthaceae
Andrographis paniculata, known as the King
of Bitters is traditionally used in Indian systems of medicines.
Active principle: Anodrographolides.
Medicinal importance : Androgrophis is a potent hepatoprotective and is widely used to treat liver
disorders. Concoction of Andrographis
paniculata and eight other hers
(Nilavembu Kudineer) is effectively used to treat malaria and dengue.
33. Differentiate bio-medicines
and botanical medicines.
Answer: Medicinally useful molecules obtained from plants that are
marketed as drugs are called Biomedicines. Medicinal plants which are marketed
as powders or in other modified forms are known as Botanical medicines.
34. Write the origin and area of
cultivation of green gram and red gram.
Answer: Green gram
Botanical name : Vigna radiata
Origin and Area of cultivation : Green gram is a
native of India and the earliest archaeological evidences are found in the
state of Maharashtra. It is cultivated in the states of Madhya Pradesh,
Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
Red gram / Pigeon pea
Botanical name: Cajanus cajan
Origin and Area of cultivation: It is the only pulse
native to Southern India. It is mainly grown in the states of Maharashtra,
Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka and Gujarat.
35. What are millets? What are
its types? Give example for each type.
Answer: The term millet is applied to a variety of very small
seeds originally cultivated by ancient people in Africa and Asia. They are
gluten free and have less glycemic index.
Types of Millets:
(a) Pearl Millet
Botanical name : Pennisetum americanum
(b) Finger Millet - Ragi
Botanical name : Eleusine coracana
(c) Sorghum
Botanical name : Sorghum vulgare
Minor Millets:
(d) Little Millet
Botanical name : Panicum sumatrense
(e) Foxtail Millet
Botanical name : Setaria italica
(f) Kodo Millet
Botanical name : Paspalum scrobiculatum
36. Write the economic importance
of Lycopersicon esculentum.
Answer: The common name of Lycopersicon
esculentum is Lady's finger. The fresh and green tender fruits are used as
a vegetable. Often they are sliced and dehydrated to conserve them for later
use. It has most important nutrients.
37. If a person drinks a cup of
coffee daily it will help him for his health. Is this correct? If it is
correct, list out the benefits.
Answer: Drinking coffee in moderation provides the following
health benefits:
(i) Caffeine enhances release of acetylcholine in brain, which
in turn enhances efficiency.
(ii) It can lower the incidence of fatty liver diseases,
cirrhosis and cancer. It may reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
38. Enumerate the uses of
turmeric.
Answer: Turmeric is used as a spice and also has medicinal
properties.
(i) Turmeric is one of the most important and ancient Indian
spices and used traditionally over thousands of years for culinary, cosmetic,
dyeing and for medicinal purposes.
(ii) It is an important constituent of curry powders.
(iii) Turmeric is used as a colouring agent in pharmacy,
confectionery and food industry. Rice coloured with turmeric (yellow) is
considered sacred which is used in ceremonies.
(iv) It is also used for dyeing leather, fibre, paper and toys.
Medicinal properties
(i) Curcumin extracted from turmeric is responsible for the
yellow colour. Curcumin is a very good anti-oxidant which may help fight
various kinds of cancer.
(ii) It has anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic, anti-bacterial, anti-fungal
and antiviral activities.
(iii) It stops platelets from clotting in arteries, which leads
to heart attack.
(iv) It is used to treat Alzheimer’s
disease due to its property to cross over blood brain barrier.
(v) It is one of the traditional medicines used for wound
healing.
39. What is TSM? How does it
classified and what does it focuses on?
Answer: Traditional Systems
of Medicines (TSM):
(i) India has a rich medicinal heritage. A number of
Traditional Systems of Medicine (TSM) are practiced in India some of which come
from outside India.
(ii) TSM in India can be broadly classified into institutionalized or documented and non-institutionalized or oral
traditions.
(iii) Institutionalized Indian systems include Siddha and
Ayurveda which are practiced for about two thousand years.
(iv) These systems have prescribed texts in which the symptoms,
disease diagnosis, drugs to cure, preparation of drugs, dosage and diet
regimes, daily and seasonal regimens.
(v) Non-institutional systems, whereas, do not have such
records and are practiced by rural and tribal peoples across India.
(vi) The knowledge is mostly held in oral form. The TSM focus on
healthy lifestyle and healthy diet for maintaining good health and disease
reversal.
40. What are the advantages of
cultivation of aromatic plants?
Answer: Profitable cultivation of medicinal plants can be
practiced by the entrepreneurs along with traditional agriculture horticulture
crops. They can be profitably inter cropped in plantations. Cultivation of
medicinal/aromatic plants offers following advantages:
(i) Generate employment through development of ancillary
industries.
(ii) Foreign exchange earnings through exports.
(iii) Crops are not damaged by domestic animals or by birds.
(iv) Technologies are farmer and eco-friendly.
41. How will you make a Bonsai
tree
Answer: Bonsai is a Japanese art form using miniature trees grown
in containers that mimic the shape and scale of full size trees.
Procedure
(i) Visualize the finished product of bonsai while selecting a
plant species and the pot.
(ii) Plug out the sapling and clean and prune the roots.
(iii) Prepare the pot and position the tree in it.
(iv) After re-potting leave the plant in a semi shaded area
until the roots have re-established.
The common Bonsai
styles are
a. Formal Upright
b. Informal Upright
c. Broom style
d. Slant
e. Cascade - Overflowing potential of growth
f. Semi Cascade
42. What is NMPB?
Answer: (i) Government of India has set up National Medicinal Plants Board (NMPB) on 24th
November 2000. Currently this board is working under AYUSH Government of India.
(ii) Developing an apt mechanism for coordination of various
ministries and implementation of policies for overall growth of medicinal plant
sector both at central / state and international level is the primary mandate
of NMPB.
(iii) It focusses on in-situ and ex-situ conservation and
enhancing local medicinal plants and aromatic species of medicinal significance
to meet the growing demand.
43. Write the uses of nuts you
have studied.
Answer: Cashew nut
Botanical name : Anacardium
occidentale
Nuts are simple dry
fruits composed of a hard shell and an edible kernel. They are packed with a
good source of healthy fats, fibre, protein, vitamins, minerals and
antioxidants.
Example : Cashew nut
Uses:
(i) Cashews are commonly used for garnishing sweets or curries,
or ground into a paste that forms a base of sauces for curries or some sweets.
(ii) Roasted and raw kernels are used as snacks.
Almond
Botanical name : Prunus dulcis
Uses:
(i) Almonds are often eaten raw or roasted and are available
as whole, sliced (flaked), and as flour.
(ii) Almond oil is made into almond butter or almond milk,
which are used in sweet and savoury dishes.
(iii) Almond helps in promoting HDL (High Density Lipids).
44. Give an account on the role
of Jasminum and Rosa in perfuming.
Answer: Jasminum :
(i) The essential oil is present in the epidermal cells of the
inner and outer surfaces of both the sepals and petals. One ton of Jasmine
blossom yields about 2.5 to 3 kg of essential oil.
(ii) Jasmine flowers have been used since ancient times in India
for worship, ceremonial purposes, incense and fumigants, as well as for making
perfumed hair oils, cosmetics and soaps.
(iii) Jasmine oil is an essential oil that is valued for its
soothing, relaxing, antidepressant qualities.
(iv) Jasmine blends well with other perfumes. It is much used in
modern perfumery and cosmetics and has become popular in air freshners,
anti-perspirants, talcum powders, shampoos and deodorants.
Rose :
(i) Rose oil is one of the oldest and most expensive of perfume
oils. The oil is concentrated in the epidermal cells on the inner surface of
the petals.
(ii) Rose oil is largely used in perfumes, scenting soaps,
flavouring soft drinks, liqueurs and certain types of tobacco, particularly
snuff of chewing tobacco.
(iii) Rose water (panneer) containing much of phenylethyl
alcohol and other compounds in dissolved confectioneries syrups and soft
drinks.
(iv) In India, the water is much used in eye lotions and
eye-washes. In addition, it is sprinkled on guests as a ceremonial welcome.
45. Give an account of active
principle and medicinal values of any two plants you have studied.
Answer: Medicinal Plants:
(i) Medicinally useful molecules obtained from plants that are
marketed as drugs are called Biomedicines.
(ii) Medicinal plants which are marketed as powders or in other
modified forms are known as Botanical medicines.
Keezhanelli
Botanical name: Phyllanthus amarus
Origin and Area of cultivation: The plant is a native
of Tropical American region and is naturalised in India and other tropical
countries.
Active principle:
Phyllanthin is the
major chemical component.
Medicinal importance:
Phyllanthus is a
well-known hepato-protective plant generally used in Tamil Nadu for the
treatment of Jaundice. It has been scientifically proved that the extract of P.
amarus is effective against hepatitis B virus.
Adathodai
Botanical name: Justicia adhatoda.
Origin and Area of cultivation: It is native to India
and Srilanka.
Active principle: Vascin
Uses:
Adhatoda possess
broncho dilating property. The decoction is used in treating many bronchial
disorders such as cough, cold and asthma. It is also used in treating fevers.
The extract forms an ingredient of cough syrups.
46. Write the economic importance
of rice.
Answer: (i) Rice is the
easily digestible calorie rich cereal food which is used as a staple food in
Southern and North East India. Various rice products such as Flaked rice, Puffed rice / parched rice are used as
breakfast cereal or as snack food in different parts of India.
(ii) Rice bran oil
obtained from the rice bran is used in culinary and industrial purposes.
(iii) Husks are used
as fuel, and in the manufacture of packing material and fertilizer.
47. Which TSM is widely practiced
and culturally accepted in Tamil Nadu? - explain.
Answer: Siddha system of medicine:
(i) Siddha is the most popular, widely practiced and culturally
accepted system in Tamil Nadu. It is based on the texts written by 18 Siddhars.
(ii) There are different opinions on the constitution of 18
Siddhars. The Siddhars are not only from Tamil Nadu, but have also come from
other countries.
(iii) The entire knowledge is documented in the form of poems in
Tamil. Siddha is principally based on the Pancabuta
philosophy.
(iv) According to this system three humors namely Vatam, Pittam and Kapam are responsible for the health of human beings and any
disturbance in the equilibrium of these humors result in ill health.
(v) The drug sources of
Siddha include plants, animal parts, marine products and minerals. This system
specializes in using minerals for preparing drugs with the long shelf-life.
(vi) This system uses about 800 herbs as source of drugs. Great
stress is laid on disease prevention, health promotion, rejuvenation and cure.
48. What are psychoactive drugs?
Add a note Marijuana and Opium
Answer: Phytochemicals / drugs from some of the plants alter an
individual’s perceptions of mind by producing hallucination are known as
psychoactive drugs.
Opium poppy
Botanical name: Papaver somniferum
Opium is derived from
the exudates of fruits of poppy plants. It was traditionally used to induce
sleep and for relieving pain. Opium yields Morphine,
a strong analgesic which is used in surgery. However, opium is an addiction
forming drug.
Cannabis / Marijuana
Botanical name: Cannabis sativa
(i) The active principle in Marijuana is trans-tetrahydrocanabinal (THC). It possess a number of medicinal
properties. It is an effective pain reliever and reduces hypertension.
(ii) THC is used in treating Glaucoma a condition in which pressure develops in the eyes.
(iii) THC is also used in reducing nausea of cancer patients
undergoing radiation and chemotherapy.
(iv) THC provides relief to bronchial disorders, especially asthma
as it dilates bronchial vessels.
(v) Because of these medicinal properties, cultivation of
cannabis is legalized in some countries. However, prolonged use causes
addiction and has an effect on individual’s health and society.
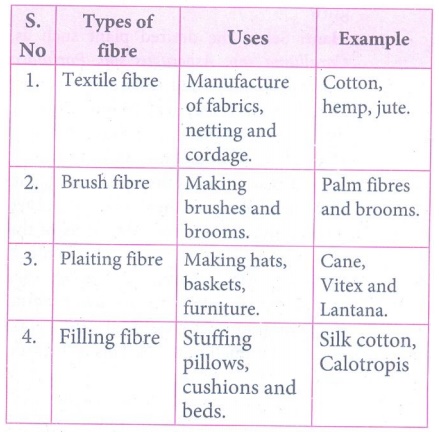
49. Describe the types of fibres.
Answer: Botanically a fiber is a long narrow and thick- walled
cell. Plant fibres are classified according to their use below:
50. What are the King and Queen
of spices? Explain about them and their uses.
Answer: Cardamom is called as “Queen of Spices”. In India it is
one of the main cash crops cultivated in the Western Ghats, and North Eastern
India.
Botanical name: Elettaria cardamomum
Uses :
(i) The seeds have a pleasing aroma and a characteristic warm,
slightly pungent taste.
(ii) It is used for flavouring confectioneries, bakery products
and beverages.
(iii) The seeds are used in the preparation of curry powder,
pickles and cakes.
(iv) Medicinally, it is employed as a stimulant and carminative.
(v) It is also chewed as a mouth freshener.
Black Pepper
Botanical name: Piper nigrum
Pepper is one of the
most important Indian spices referred to as the “King of Spices” and also termed as “Black Gold of India”. Kerala, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu are the top
producers in India. The characteristic pungency of the pepper is due to the
presence of alkaloid Piperine. There are two types of pepper available in the
market namely black and white pepper.
Uses :
(i) It is used for flavouring in the preparation of sauces,
soups, curry powder and pickles.
(ii) It is used in medicine as an aromatic stimulant for
enhancing salivary and gastric secretions and also as a stomachic.
(iii) Pepper also enhances the bio-absorption of medicines.
51. How will you prepare an
organic pesticide for your home garden with the vegetables available from your
kitchen?
Answer: Preparation of Organic Pesticide
(i) Mix 120g of hot chillies with 110 g of garlic or onion.
Chop them thoroughly.
(ii) Blend the vegetables together manually or using an electric
grinder until it forms a thick paste.
(iii) Add the vegetable paste to 500 ml of warm water. Give the
ingredients a stir to thoroughly mix them together.
(iv) Pour the solution into a glass container and leave it
undisturbed for 24 hours. If possible, keep the container in a sunny location.
If not, at least keep the mixture in a warm place.
(v) Strain the mixture. Pour the solution through a strainer,
remove the vegetables and collect the vegetable-infused water and pour into
another container. This filtrate is the pesticide. Either discard the
vegetables or use it as a compost.
(vi) Pour the pesticide into a squirt bottle. Make sure that the
spray bottle has first been cleaned with warm water and soap to get rid it of
any potential contaminants. Use a funnel to transfer the liquid into the squirt
bottle and replace the nozzle.
(vii) Spray your plants with the pesticide. Treat the infected
plants every 4 to 5 days with the solution. After 3 or 4 treatments, the pest
will be eliminated. If the area is thoroughly covered with the solution, this
pesticide should keep bugs away for the rest of the season.
52. What will you do if you want
to make a portable indoor greenery?
Answer: A terrarium is a collection of small plants growing in a
transparent, sealed container, Terrariums are easy to make, low maintenance gardens,
and it can survive indefinitely with minimal water.
Procedure :
(i) Collect any interesting glassware or container you have /
from store and clean it thoroughly. Plan to arrange the plants inside the
glassware.
(ii) Add Drainage
Layers: To create a false drainage layer, fill the bottom with pebbles so
that water can settle and does not flood. The depth of the pebbles depends on
the size of the container.
(iii) Add the Activated Charcoal: Cover the pebbles
with charcoal to improve the quality of the terraria by reducing bacteria,
fungi and odors.
(iv) Add Soil: Add enough soil so that the plant roots will have enough
space to fit and grow.
(v) Plant: Select the desired plant such as, Caralluma spp, Asperagus spp,
Portulaca spp, Begonia spp, and Chlorophytum
spp; trim the roots if they are too long. Dig a pit using a stick, and
place the plants’ roots in it. Add more soil around the top and compact the
soil down around the base of the plant. Place little plants in the container
and try to keep them away from the edges of the container, so that the leaves
do not touch the sides. After planting add accessories like a layer of moss
(dried or living), little figurines (old toys, glass beads, stones) or a layer
of miniature rocks. This is the little green world
(vi) Cleaning and Watering: Wipe if there is any
dirt along the sides of the container. Give the terrarium a little bit of water
and enjoy the beautiful miniature living world on your table or in your living
room. Ready made terrariums can fetch a good price as indoor garden objects or
as gift articles.
53. Give an account on
cultivation of Gloriosa superba / Cymbopogon citrates
Answer: Cultivation of
Medicinal Plant - Gloriosa superba:
Soil and Climate: Red loamy soils are well suited for cultivation.
Planting: It is distributed from June - July. Plough the field 2 - 3
times and add 10 tons of Farmyard Manure during last ploughing. Trenches of 30 cm
depth are formed and tubers are planted at 30 - 45 cm spacing. The vines are
trained over support.
Irrigation: Irrigation should be given immediately after planting.
Subsequent irrigation is given at 5 days intervals of time.
Harvest: Pods are harvested at 160 - 180 days.
Cultivation of Aromatic plant (Cymbopogon citratus (Lemongrass).
Soil and Climate: Lemongrass grow well in full sun, with plenty of water, in
a rich, well-draining soil.
Planting: This plant can thrive well all through the year. Fill
planting holes with composted manure to improve fertility and enhance the
soil’s ability to hold water. If you’re adding several lemongrass plants to
planting beds, space plants 60 cm apart.
Irrigation: Based on the soil, water requirements for this plant will
vary. Sandy, loose soils require more frequent watering than silty loam.
Harvest: Start harvesting when plants are 30 cm tall and stem bases
are at least 1.5 cm thick. Cut stalks at ground level.
Related Topics