Chapter: C# and .NET Framework
Simple and Complex Data Binding
Simple
and Complex Data Binding
What is
DataBinding?
DataBinding
is a powerful feature provided by the .NET framework that enables visual
elements in a client to connect to a datasource such as DataSets, DataViews,
Arrays etc. Some of the visual elements in the client can be TextBox, Datagrid
etc. A two-way connection is established such that any changes made to the
datasource are reflected immediately in the visual element and vice versa.
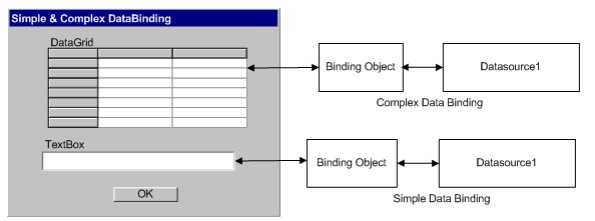
Below is
a graphical description of the concept of databinding:
DataBinding
Before .NET
In the
earlier databinding models, the datasource that could be used was usually
limited to a database. All DBMS systems provided their own API's to help in
building GUI applications and quickly bind them to the data. Programmer did not
have the flexibility to control the databinding process with the result that
most developers avoided the use of databinding.
DataBinding
with .NET
The .NET
framework provides a very flexible and powerful approach to databinding and
allows the programmer to have a fine control over the steps involved in the
whole process. One of the biggest improvements with .Net has been the
introduction of databinding to web pages through the use of .Net server-side
web controls. Hence, building data driven web applications has been greatly
simplified. Please note that this article only deals with data binding in .NET
windows forms.
Advantages
of DataBinding
1. Databinding
in .NET can be used to write data driven applications quickly. .NET data
binding allows you to write less code with fast execution but still get the
work done in the best way.
2. .NET automatically writes a lot of databinding code for you in the
background (you can see it in "Windows Generated Code" section), so
the developer does not have to spend time writing code for basic databinding,
but still has the flexibility of modifying any code that he would like to. We
get the benefits of bound as well as unbound approach.
3. Control
over the Databinding process by using events. This is discussed in more detail
later in the article.
Disadvantages
of DataBinding
1. More optimized code can be written by
using the unbound or traditional methods.
2. Complete
flexibility can only be achieved by using the unbound approach.
Databinding
Concepts
For
databinding to take place data provider and a data consumer should exist so
that a synchronized link is established between the two. Data providers contain
the data and the data consumers use the data exposed by the data providers and
display them.
.NET has
expanded the scope of possible data providers. In .NET any class or component
that implements the IList interface is a valid DataSource. If a component
implements the IList interface then it is transformed into an index based
collection.
Some of
the classes that support the IList interface in the NET framework are given
below. Please note that any class that implements the IList interface is a
valid data provider.
1. Arrays
2. DataColumn
3. DataTable
4. DataView
5. DataSet
Please
note that IList interface only allows you to bind at run time. If you want to
support DataBinding at design time you will have to implement the IComponent
interface as well. Also note that you cannot bind to DataReaders in windows
forms (you can in web forms).
The .NET
framework supports simple and complex DataBinding. Simple databinding is
supported by controls like TextBoxes. In Simple databinding, only one data
value can be displayed by the control at a time. In complex databinding, which
is supported by controls like the DataGrid, more than one data value from the
DataSource can be displayed.
Dataflow
during DataBinding
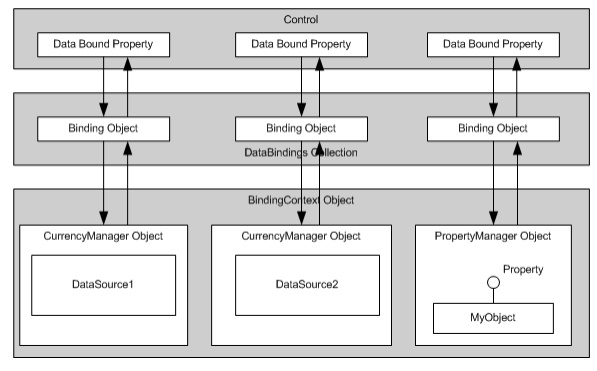
A good
understanding of the dataflow from the control to the datasource is very
important. The diagram below gives an overview of the dataflow and the objects
involved.
In .NET,
controls can have many properties that can be bound to a DataSource. Each
databound property has an associated Binding object. Since a control can have
many Binding objects, the control has a collection (instance of
ControlBindingsCollection class) of all the Binding objects. Also remember that
different properties of the same control can be bound to different
datasource's.
Each
Binding object talks to a CurrencyManager or a PropertyManager. CurrencyManager
and PropertyManager classes merit a little explanation, as they are important.
CurrencyManager and PropertyManager are derived from the base class
BindingManagerBase. The purpose of BindingManagerBase class is to maintain the
concurrency between the datasource and the control. Of the two classes, the
CurrencyManager is used when the datasource implements the IList Interface.
Examples of such datasources are DataView, DataSet, ArrayList etc. The
CurrencyManager can be used for simple as well as complex databinding. However,
the PropertyManager is used when the datasource is an instance of a
user-defined class. The Control's property is bound to the property exposed by
this object. PropertyManager can only be used for simple databinding.
As a rule
of thumb if you want your class to be a datasource, you should use
CurrencyManager when your class is a data container. However, if you are
interested in binding a control to properties exposed by your own class, then
using a PropertyManager is easier, since you do not have to implement the IList
Interface.
Since a
form can contain many controls each binding to a different datasource, a class
is needed to manage the CurrencyManager and PropertyManager objects. Therefore,
each windows form in .NET has a default BindingContext object associated with
it. But, you can always create more BindingContext objects on the form. The
BindingContext object is a collection of CurrencyManager and PropertyManager
objects.
Related Topics