Chapter: C# and .NET Framework
C# Operators
OPERATORS
C# Operators
Ø C#
provides a large set of operators, which are symbols that specify which
operations to perform in an expression. Operations on integral types such as ==, !=, <, >, <=, >=, binary +, binary -, ^,
&, |, ~, ++, --, andsizeof() are generally allowed on enumerations. In addition, many operators can be overloaded by the user, thus changing their meaning when
applied to a user-defined type.
Ø The
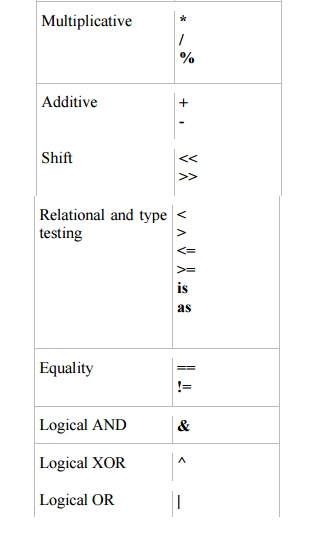
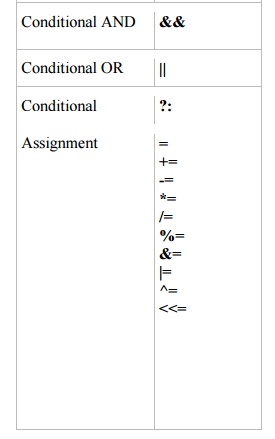
following table lists the C# operators grouped in order of precedence.
Operators within each group have equal precedence.

Arithmetic
Overflow
The arithmetic operators (+, -, *, /) can
produce results that are outside the range of possible values for the numeric
type involved. You should refer to the section on a particular operator for
details, but in general:
• Integer arithmetic overflow either throws
an Overflow Exception or discards the most significant bits
of the result. Integer division by zero always throws a DivideByZeroException.
• Floating-point arithmetic overflow or
division by zero never throws an exception, because floating-point types are
based on IEEE 754 and so have provisions for representing infinity and NaN (Not
a Number).
• Decimal arithmetic overflow always
throws an OverflowException. Decimal division by zero always throws a
DivideByZeroException.
When integer overflow occurs, what
happens depends on the execution context, which can be checked or unchecked. In
a checked context, an OverflowException is thrown. In an unchecked context, the
most significant bits of the result are discarded and execution continues. Thus,
C# gives you the choice of handling or ignoring overflow.
In addition to the arithmetic operators,
integral-type to integral-type casts can cause overflow, for example, casting a
long to an int, and are subject to checked or unchecked execution. However,
bitwise operators and shift operators never cause overflow.
DECLARATION OF PRIMITIVE DATA TYPES IN C#
Data Type
Ø The type
of data that a variable contains is called Data Type (type). A Data Type is a
classification of things that share similar type of qualities or
characteristics or behavior.
Ø C# is
strongly typed language so every variable and object must have a type.
There are two types of data type
in C#
1.
primitive
types (or) predefined
Ex: byte, short, int, float, double, long ,char,
bool, DateTime, string, object etc..
2.
non-primitive
types (or) User Defined
Ex: class
, struct , enum , interface, delegate,
array.
In C#,
based on what a variable contains there is two types of built-in data type
Value types
Ø A
variable holds actual values then that type of data types are value types.
These value types are stored in ―stack‖ memory and these value types are fixed
in size. If you assign a value of a variable to another variable it will create
two copies.
Ex: byte,
short, int, float, double, long ,char, bool, DateTime.
·
Primitive data types are value types except string,
object.
·
Object type is superior to all types. It can store
any type or any size of data. It helps in inheritance process.
·
Struct, enum are value types.
Reference types
Ø A
variable holds a reference to the value, then that type of data types are
reference types.
Ø These
reference types are stored in ―heap‖ memory and these types are not fixed in
size.
Ø They are
maintained in system managed heap but it also uses stack to store reference of
the heap.
Ø Two
primitive types (string and object) and non-primitive data types (class,
interface & delegate) are examples of reference type.
Ex: class,
interface, delegate, string, object and array
Date and Time
Date time
is one of the most commonly used data type in C#.
Ex:
DateTime currenttime = DateTime.Now;//display’s current date time.
Output:
current time: 6/13/2015 4:50:45 pm
int days = DateTime.DaysInMonth(2011, 7);// it displays ―31‖.
Output:
No of
days 31
Related Topics