Chapter: C# and .NET Framework
C# Multithreading
MULTITHREADING
Ø Multithreading
is a feature provided by the operating system that enables your application to
have more than one execution path at the same time. Technically, multithreaded
programming requires a multitasking operating system.
Ø Let’s
understand this concept with a very basic example. Everyone has used Microsoft
Word. It
takes input from the user and displays it on the screen in one thread while it
continues to check spelling and grammatical mistakes in another thread and at
the same time another thread saves the document automatically at regular
intervals.
Now let’s
understand a program. In this program we will try to implement the concept of
multithreading and will define multiple concurrent execution paths.
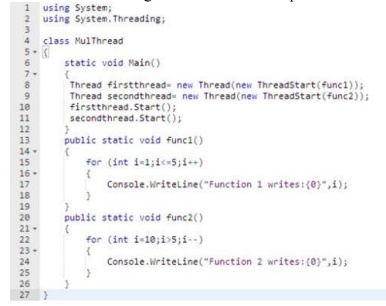
Now
through the use of threads, we cannot be sure of the sequence of the output
program. Now if you write this program without the threading concept, like
this:
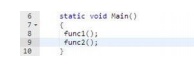
You will
see that func2() will execute only after func1() and in the first program you
will be able to execute both functions simultaneously.
The
thread class provides a number of useful methods and properties to control and
manage thread execution.
Most Commonly used Static Member of System.Threading.Thread
class
The
following are the most commonly used static members of the
System.Threading.Thread class:
·
CurrentThread(): gives a
reference to the currently executing thread
·
Thread.Sleep(): cause
the currently executing thread to pause temporarily for the specified amount of time
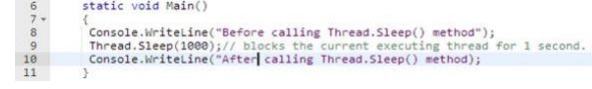
When you
execute the preceding program, you will notice a delay of 1 second between the
printing of the two lines.
Most Common Instance Member of the
System.Threading.Thread class
The
following are the most common instance members of the System.Threading.Thread
class:
·
Name
A property of
string type used to
get/set the friendly name
of the thread
instance.
·
Priority
A
property of type System.Threading.ThreadPriority to schedule the priority of
threads.
·
IsAlive
A Boolean property indicating whether the thread is alive or terminated.
·
ThreadState
A
property of type System.Threading.ThreadState, used to get the value containing
the state of the thread.
·
Start()
Starts the execution of the thread.
·
Abort()
Allows the current thread to stop the execution of the thread permanently.
·
Suspend()
Pauses
the execution of the thread temporarily.
·
Resume()
Resumes
the execution of a suspended
thread.
·
Join()
Make the
current thread wait for another thread to finish.
Related Topics