Chapter: C# and .NET Framework
Structure of .NET Framework
STRUCTURE
OF .NET FRAMEWORK
The
Microsoft .Net Framework is a new computing platform that provides tools and
technologies need to build networked applications as well as distributed web
services and web applications.
Ø The .Net
Framework provides the necessary compile time and run time foundation to build
and run any language that conforms to the Common Language Specification(CLS)
Components of .Net Framework
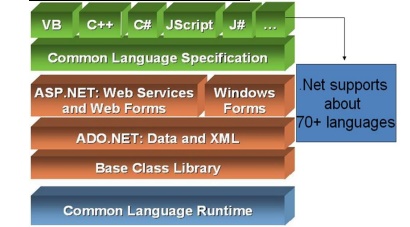
Ø Net
Framework is a platform that provides tools and technologies to develop
Windows, Web and Enterprise applications. It mainly contains two components,
1. Common
Language Runtime (CLR)
2. .Net
Framework Class Library
Common Language Runtime (CLR)
.Net Framework provides runtime
environment called Common Language Runtime (CLR).It provides an environment to run
all the .Net Programs.
The code which runs under the CLR
is called as Managed Code.
Programmers need not to worry on
managing the memory if the programs are running under the CLR as it provides
Programmatically, when our program needs memory, CLR allocates the memory for
scope and de-allocates the memory if the scope is completed.
Language Compilers (e.g. C#,
VB.Net, J#) will convert the Code/Program to Microsoft
Intermediate memory management and
thread management. Language (MSIL)
intern this will be converted to Native Code by CLR.
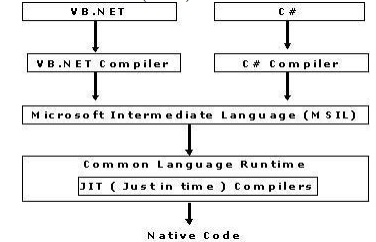
There are
currently over 15 language compilers being built by Microsoft and other
companies also producing the code that will execute under CLR.
Net Framework Class Library (FCL)
Ø This is
also called as Base Class Library and it is common for all types of
applications i.e. the way you access the Library Classes and Methods in VB.NET
will be the same in C#, and it is common for all other languages in .NET.
Ø The
following are different types of applications that can make use of .net class
library.
1. Windows Application.
2. Console Application
3. Web Application.
4. XML Web Services.
5. Windows Services.
Common Type System (CTS)
Ø It
describes set of data types that can be used in different .Net languages in
common. (i.e), CTS ensures that objects written in different .Net languages can
interact with each other.
Ø For
Communicating between programs written in any .NET complaint language, the type
have to be compatible on the basic level.
The common type system supports two general categories of types:
Value
types:
Value
types directly contain their data, and instances of value types are either
allocated on the stack or allocated inline in a structure. Value types can be
built-in (implemented by the runtime), user-defined, or enumerations.
Reference
types:
Reference
types store a reference to the value's memory address, and are allocated on the
heap. Reference types can be self-describing types, pointer types, or interface
types. The type of a reference type can be determined from values of
self-describing types. Self-describing types are further split into arrays and
class types. The class types are user-defined classes, boxed value types, and
delegates.
CommonLanguageSpecification(CLS)
It is a
sub set of CTS and it specifies a set of rules that needs to be adhered or
satisfied by all language compilers targeting CLR. It helps in cross language
inheritance and cross language debugging.
Commonlanguagespecification
Rules:
It
describes the minimal and complete set of features to produce code that can be
hosted by CLR. It ensures that products of compilers will work properly in .NET
environment.
Sample Rules:
·
Representation of text strings
·
Internal representation of enumerations
·
Definition of static members and this is a subset
of the CTS which all .NET languages are expected to support.
·
Microsoft has defined CLS which are nothing but
guidelines that language to follow so that it can communicate with other .NET
languages in a seamless manner.
Related Topics