Chapter: C# and .NET Framework
Important Short Questions and Answers: C# Basics
1.
Define in
brief Object Oriented Principles.
Ø OOP is
based on three key principles: encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.
Ø Encapsulation binds together code and data,
Ø Inheritance is the mechanism by which one
class can inherit the functionality of another.
Ø Polymorphism lets you define one interface
that describes a general set of actions.
Ø These
attributes work together in a powerful way that enables the construction of
reliable, reusable, and extensible programs.
2.
What are
the applications of C# ?
·
console applications
·
Windows applications
·
Developing windows controls
·
Developing ASP.NET projects
·
Creating Web Controls
·
Providing web services
·
Developing .NET component library
3.
What is
c#?
Ø C# is
Microsoft premium language for .Net development such as Enterprise
applications, web applications , windows applications and embedded systems.
Ø C# is
intended to be a simple, modern, general- purpose , type safe object oriented
programming language that enables programmers to quickly and easily build
solutions for the Microsoft .Net platform.
Ø A
programming infrastructure created by Microsoft for building, deploying, and
running applications and services that use .NET technologies, such as desktop
applications and Web services.
4.
Draw the
structure of .Net Framework.
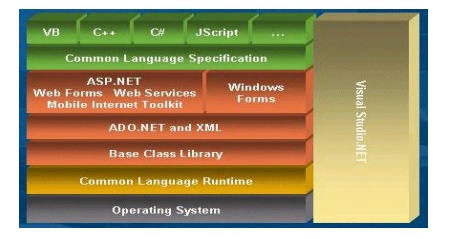
5. What are boxing and unboxing?
Boxing:
The
operation of converting a value type to a reference type is called boxing
Example:
int
i=123;
object
obj=(object)i;
Unboxing:
The operation of converting a reference type to a value type is called
unboxing.
Example:
Object
obj=123; int i=(int)obj;
6. How C #does differ from Java?
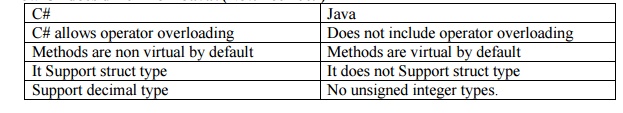
C#
C# allows
operator overloading
Methods
are non virtual by default
It
Support struct type
Support
decimal type
Java
Does not
include operator overloading
Methods
are virtual by default
It does
not Support struct type
No
unsigned integer types.
7. Name any four applications that are
supported by .Net platform.
Ø Console Applications
Ø Windows Applications Ø Creating web controls Ø Providing web services
Ø Developing .net component library.
8. Compare value type and reference type.
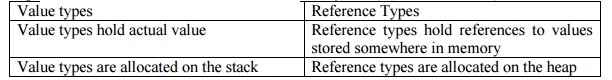
Value types
Value
types hold actual value
Value
types are allocated on the stack
Reference Types
Reference
types hold references to values stored somewhere in memory
Reference
types are allocated on the heap
9. What are the basic elements of C#?
Ø Formatting
Ø Designing
Ø Naming
Ø Packaging
Ø Documentation
Ø Programming
10.
List out
the different types of I/O Commands in c#.
Ø Command
Line Arguments
Ø Readline
Method
Ø Compilation
error
11.
Give the
benefits of .NET framework.
Ø Simple
Ø Consistent
Ø Modern
Ø Object
Oriented
Ø Type-safe
12.
Discuss
.NET namespaces
The .NET
Framework Class Libraries(FCL) are arranged into a logical grouping according
to their functionality and usability is called Namespaces.
13. Is it possible to have two main () in a C#
code? If so, how it is resolved?
Yes, If
the program contains several mains that could be the startup function then you
need to specify which to use, either on the command line or in a project
properties application startup object.
14.
What are
the types of string?
Ø Immutable
String
Ø Mutable
String
Ø Regular
Expression
15.
List out
the advantages of using the methods.
Ø Reducing
duplication of code
Ø Decomposing
complex problems into simpler pieces.
Ø Improving
clarity of the code
Ø Reuse of
code
Ø Information
hiding
16.
What are
the types of branching?
Conditional Branching
Conditional
branching is the branching is based on particular condition.
Unconditional Branching
Unconditional
branching is the branching without any decision
17. Give
the syntax of foreach loop. foreach(type<iteration
variable>in list)
{
Statements;
}
18. How is class declared?
Classes
are declared by using the keyword class followed by the class name and the set
of class members surrounded by curly braces.
Syntax:
[modifiers]class
class_name
{
[Class
members declaration;]
}
19. How are the class members accessed?
Once the
object are created, the dot operator is used to access any class members by
using the object name.
Syntax:
To access
the variables inside the class
Objectname.variable
name;
To call
the method inside the class
Objectname.methodname(argument_list)
Related Topics