Effects, Types, Management | First Aid | Nursing - Shock | 11th Nursing : Chapter 9 : First Aid
Chapter: 11th Nursing : Chapter 9 : First Aid
Shock
Shock
Shock is a life-
threatening condition in which not enough blood is reaching the vital organs in
the body as a result of injury or illness.
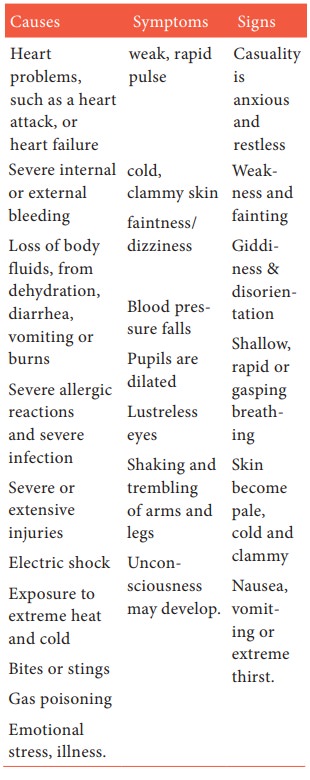
Effects of shock
·
Early loss of consciousness
·
Failing heart output and insufficient oxygen to cells that are
vital for survival.
· Sustained lowered blood pressure
Types of Shock
Neurogenic Shock
From damage to the nervous system such as a severed spine or a brain injury.
Haemorrhagic Shock
Loss of blood due to wound and internal bleeding.
Respiratory Shock
Insufficient amount of oxygen in the blood due to inadequate breathing.
Cardiogenic Shock
Cardiac muscle not pumping effectively due to injury or previous heart attack.
Circulatory shock,
It is a life-threatening medical condition of low blood perfusion to tissues resulting in cellular injury and inadequate tissue function.
Hypovolemic shock
Related to low bloodvolume from hemorrhage, internal bleeding, severe dehydration, vomiting, diarrhea, uncontrolled diabetes, large areas of severely-burned skin, or extreme heat stress.
Metabolic
Loss of body fluids with a change in biochemical equilibrium
Septic Shock
Toxin causes pooling of blood in capillaries not enough blood available for tissues.
Anaphylactic Shock
Severe allergic reaction of the body to sensitization by a foreign protein caused by an allergic reaction to a food, drug, or venom.
Traumatic shock
Brought on by either a traumatic physical injury such as being hit by a car or a mental/emotional blow such as seeing a loved one killed.
Insulin shock
Hypoglycemic (low blood sugar) reaction to an overdose of insulin, a skipped meal, or strenuous exercise.
Electric shock
Injuries caused when electric current passes through body.
Management
a)
Immediately reassure and comfort the casuality.
b)
Normally the lower extremities should be elevated. This reduces
the blood in the extremities and improves the blood supply to the heart.
c)
If there are indications of the head injuries, the head could be
raised slightly to reduce pressure on the brain.
·
If there are breathing difficulties, the victim may be more
comfortable with head and shoulders raised
·
Loosen the tight clothing to help the circulation and assist
breathing.
·
Treat the cause of shock, stop bleeding, immobilize fracture.
·
If breathing and heart beat stop then;-
·
Establish the airway
·
Begin resuscitation immediately.
·
Keep patient in recovery position.
Follow DRSABCD and manage other severe injuries
D - Danger Ensure the area is safe.
R -Response Check for
response: ask their name, squeeze their shoulders.
S-Send for help
A – Airway Open patient’s mouth.
B-Breathing Check for breathing: look, listen and
feel.
C- CPR Start CPR:
30 chest compressions followed by 2 breaths.
D- Defibrillation
Related Topics