Morphology, Cultural Characteristics, Toxins, Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestations, Laboratory Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention - Shigella Dysenteriae (Dysentery Bacillus) | 12th Microbiology : Chapter 7 : Medical Bacteriology
Chapter: 12th Microbiology : Chapter 7 : Medical Bacteriology
Shigella Dysenteriae (Dysentery Bacillus)
Shigella Dysenteriae (Dysentery
Bacillus)
The genus
Shigellaare exclusively parasites of
human intestine and other primates. Shigella
dysenteriae is the causative agent of bacillary dysentery or shigellosis in
humans. It is a diarrheal illness which is characterized by frequent passage of
bloodstained mucopurulent stools. The four important species of the genus Shigella are: Shigella dysenteriae, Shigella
flexneri, Shigella sonnei and Shigella boydii.
Morphology
Shigella are short, Gram negative rods (0.5µm× 1–3 µm in size).
They are non – motile, non – sporing and non – capsulated (Figure 7.12).
Cultural Characteristics
• They are aerobes and facultative anaerobes.
Optimum temperature is 37°C and optimum pH – 7.4.
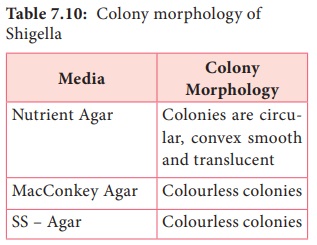
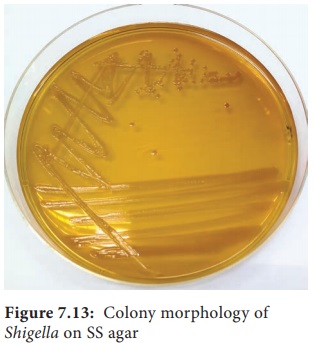
• They
can be grown on the following media and show the characteristic colony
morphology (Table 7.10 & Figure 7.13).
Toxins
Shigella dysenteriae produces toxins, which is of 3 types, namely, endotoxin, exotoxin and verocytotoxin. The mode of action of these toxins is illustrated in the Table 7.11

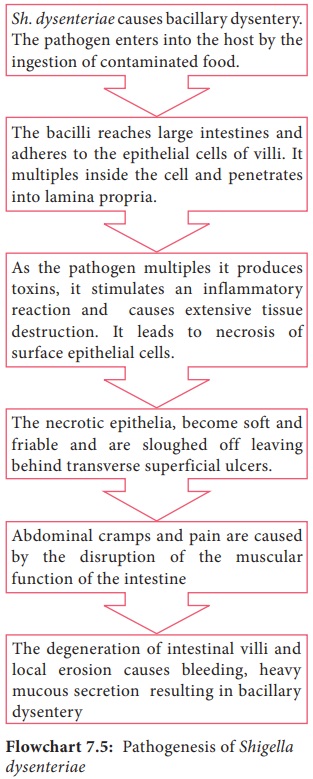
Pathogenesis
The
pathogenic mechanism of Shigella dysenteriaeis discussed below in flowchart 7.5.
Source of
Infection – Patient or carriers
Route of
entry – faecal – oral route
Site of
infection – Large intestine Incubation Period – Less than 48 hours (1–7 days)
Mode of
transmission – Food, finger, faeces and flies
Clinical Manifestations
• Frequent
passage of loose, scanty faeces containing blood and mucus.
• Abdominal
cramps and tenesmus (straining to defecate).
• Fever and vomiting.
• Hemolytic uremic syndrome (It is a condition caused by the abnormal destruction of red blood cells).
Laboratory Diagnosis
Specimens: Fresh stool is collected.
Direct
Microscopy: Saline and Lugol’s iodine preparation of faeces show large number of pus cells, and
erythrocytes.
Culture: For
inoculation, it is best to use mucus
flakes (if present in the specimen) on MacConkey agar and SS agar. After
overnight incubation at 37°C, the plates are observed for characteristic
colonies, which is confirmed by Grams staining and biochemical reactions.
Treatment and Prevention
• Uncomplicated shigellosis is a self – limiting
condition that usually recovers spontaneously.
• In acute cases, oral rehydration therapy (ORT) is
done.
• In all severe cases, the choice of antibiotic
should be based on the sensitivity of prevailing strain.
• Many strains are sensitive to Nalidixic acid and
Norfloxacin.Improving personal and environmental sanitation.
• The detection and treatment of patients and
carriers.
Related Topics