Morphology, Cultural Characteristics, Pathogenesis, Laboratory Diagnosis, Treatment - Neisseria Meningitides (Meningococcus) | 12th Microbiology : Chapter 7 : Medical Bacteriology
Chapter: 12th Microbiology : Chapter 7 : Medical Bacteriology
Neisseria Meningitides (Meningococcus)
Neisseria
Meningitides (Meningococcus)
The genus
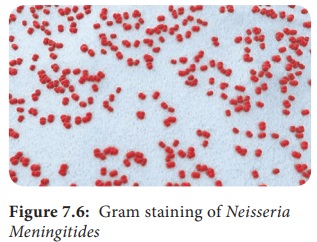
Neisseria is included in the family Neisseriaceae (Figure 7.6). It contains two important pathogens Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae, both the species
are strict human pathogens. N. meningitides causes meningococcal
meningitis (formerly known as cerebrospinal fever).
The word Meningitis
is derived from Greek word ‘meninx’
means membrane and ‘itis’ means
inflammation. It is an inflammation of meanings of brain or spinal cord.
Bacterial meningitis is a much more severe disease than viral meningitis.
Morphology
They are Gram negative diplococci (0.6µm–0.8µm in
size) arranged typically in pairs, with adjacent sides flattened.
They are non – motile, capsulated (Fresh isolates).
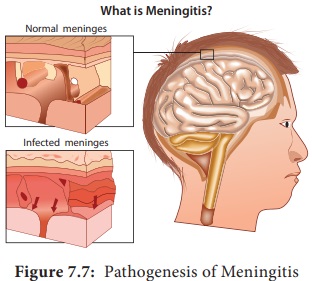
Cocci are generally intracellular when isolated
from lesions (Figure 7.7).
Cultural Characteristic
They are strict aerobes, but
growth is facilitated by 5–10% CO2 and high humidity. The
optimum temperature is 35°C–36°C and optimum pH is 7.4–7.6. They are fastidious
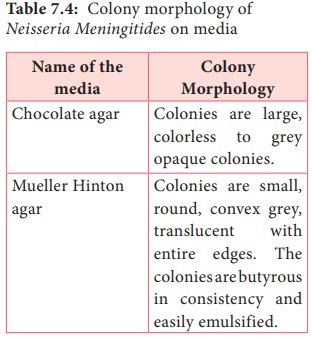
pathogens, growth occurs on media enriched with blood or serum. They grow on
the following media and show the characteristic colony morphology (Table 7.4).
Pathogenesis
N.
meningitidis is the causative agent of meningococcal meningitis, also known as pyogenic or septic
meningitis. Infection is most common in children and young adults. Meningococci
are strict human pathogens. Human nasopharynx is the reservoir of N.meningitidis. The pathogenesis is
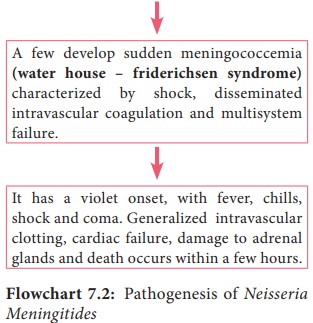
dicussed in the flowchart 7.2
Source of infection – Airborne droplets
Route of entry – Nasopharynx
Site of infection – Meninges
Incubation period – 3 days

Laboratory Diagnosis
Specimens: CSF, blood, nasopharyngeal scrapings from petechiae lesions are the specimens collected from
pyogenic meningitis patients.
Direct
Microscopy: CSF is centrifuged, and smear is prepared from the deposit for gram staining.
Meningococci are Gram negative diplococci, present mainly inside polymorphs and
many pus cells are also seen.
Culture: The
centrifuged deposit of CSF is
inoculated on chocolate agar. The plate is incubated at 36°C under 5–10% CO2
for 18–24 hours. After incubation period, meningococcusis identified by gram
staining, colony morphology and biochemical reactions. N. meningitides is catalase and oxidase positive (Figure 7.8).
Treatment and Prophylaxis
Penicillin – G is the drug of choice.
In penicillin allergic cases, chloramphenicol is recommended.
• Monovalent and polyvalent vaccies
(capsular polysaccharide) induce good immunity in older children and adults
•.Conjugate vaccines are used for
children below the age of 2 years.
Related Topics