Morphology, Culture Characteristics, Toxins, Pathogenesis, Clinical Feature, Laboratory Diagnosis, Treatment, Prophylaxis - Clostridium Tetani | 12th Microbiology : Chapter 7 : Medical Bacteriology
Chapter: 12th Microbiology : Chapter 7 : Medical Bacteriology
Clostridium Tetani
Clostridium Tetani
The genus
Clostridium consists of anaerobic,
spore forming Gram positive bacilli. The spores are wider than the bacterial
bodies, giving the bacillus a swollen appearance resembling a spindle. The name
Clostridium is derived from the word ‘kluster’ (a spindle). Most species are
saprophytes found in soil, water and decomposing plant and animal matter. Some
of the pathogens are normal flora of intestinal tract of human and animals.
The genus Clostridium
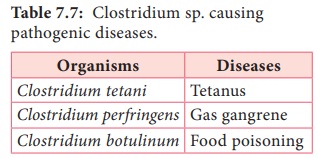
includes bacteria that causes 3 major diseases of human – Tetanus, gas gangrene and food poisoning. Clostridium pathogenicity is mainly due to production of a powerful exotoxin.
Clostridium of medical importance may be classified based on diseases they produce, which is given
the Table (7.7).
Morphology
They are
Gram positive spore forming rods. The spores are spherical and terminal in
position giving a drumstick appearance. They are motile and non – capsulated.
Culture Characteristics
• They are obligate anaerobes, optimum temperature
is 37°C and pH is 7.4.
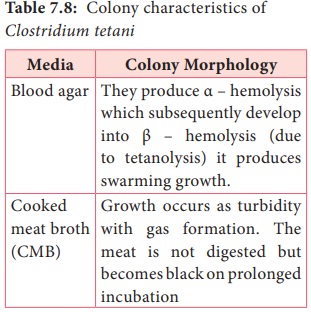
• It grows on ordinary media, but growth is enhanced by addition of blood and serum. Clostridia tetani grows on the following media and show the characteristic colony morphology (Table 7.8).
Toxins
Clostridium tetani produces
two distinct toxins namely,
a.Tetanolysis
(haemolysin)
b.Tetanospasmin (neurotoxin)
Tetanolysis
• Heat
labile and oxygen labile toxin.
• It
lysis erythrocytes and also acts as neurotoxin.
Tetanospasmin
• It is
heat labile and oxygen stable powerful neurotoxin
• It is
protein in nature. consisting of a large polypeptide chain (93,000 Dalton) and
a smaller polypeptide chain (52,000 Dalton) joined by a disulphide bond.
• Mode of Action: Tetanospasminis
a neurotoxin, which blocks the
release of inhibitory neurotransmitters (glycine and gamma – amino butyric
acid) across the synaptic junction. The toxin acts presynaptically, the
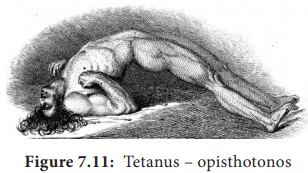
abolition of spinal inhibition causes uncontrolled spread of impulses in CNS
(Central Nerves System). This results in muscle rigidity and spasms (due to the
simultaneous contraction of agonists and antagonists, in the absence of
reciprocal inhibition Figure 7.11).
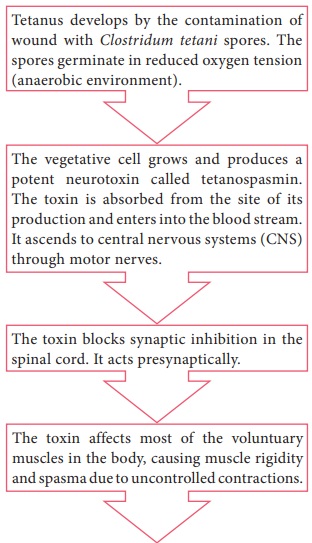
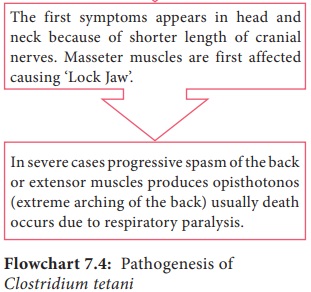
Pathogenesis
Clostridium tetani is the
causative organism of tetanus or lock
jaw disease. pathogenesis of Clostridium
tetani was discussed in detail in flowchart 7.4.
Source of
infection – Soil, dust, faeces.
Route of
entry – Through wound
Route of
entry – Through wound
Incubation period – 6–12 days
Clinical Feature
It
includes, pain and tingling at the site of wound, Lock jaw ortrismus (It is
reduced opening of the jaws), Risus sardonicus (mouth kept slightly open),
Dysphasia (impairment of the ability to speak or to understand language) and
acute asphyxia.
Laboratory Diagnosis
Specimens: Wound swab, exudates or tissue from wound.
Myth: Rust causes tetanus if introduced into a wound – for example,
by stepping on a rusty nail.
Fact: Rusty nails are more likely to be contaminated with tetanus
endospores because they have been exposed to soil and dust longer than new,
rust free nails. Any object that causes a wound, rusty or not, can inoculate
the tissue with the bacterial endospores of C. tetani. Rust itself neither
causes tetanus nor makes it worse.
Microscopy: Gram staining shows Gram positive bacilli with drumstick appearance.
Culture: The clinical specimen is inoculated on blood agar and incubated at 37°C for 24–48 hours under anaerobic conditions. The colonies are confirmed by gram staining, where it shows gram positive bacilli with drumstick appearance
Treatment
Tetanus
patients are treated in special isolated units, to protect them from noise and
light which may provoke convulsions. The spasm can be controlled by diazepam (0.1–0.2
mg/kg) injection. Antibiotic therapy with penicillin or metronidazole should be
done for a week or more.
Clostridium difficile is the causative agent of antibiotic associated colitis. It is an
acute colitis with or without pseudo membrane formation. It is animportant
complication in patients on oral antibiotic therapy. Many antibiotics have been
incriminated but lincomycin and clindamycin are particularly prone to cause
pseudomembranous colitis.
Prophylaxis
It is
done by the following methods, which are as follows.
a. Surgical prophylaxis:
It aims at removal of foreign
body, blood clots and damaged tissue in order to prevent anaerobic conditions
favorable for the germination of spores.
b. Immunoprophylaxis: Tetanus
is a preventable disease. Immune prophylaxis is of 3 types, which is given in
the (Table 7.9)

Infobits
Clostridial Toxins As Therapeutic AgentsBotulinum toxin is the
most poisonous substance known, is being used for the treatment of specific
neuromuscular disoders characterized by involuntary muscl contraction. Since
approval of Botulinu toxin (botox) by the FDA in 1989 for 3disorders –
Strabismus (crossing of th eyes), blepharospasm (spasmodic contraion of eye
muscles) and hemifacial spasm (contraction of one side of the face).
In 2000, dermatologists and plastic surgeons began using Botox
to eradicate wrinkles caused by repeated muscle contractions as we laugh, smile
or frown.
Related Topics