Chapter: Principles of Management
Role of Managers
Role of Managers
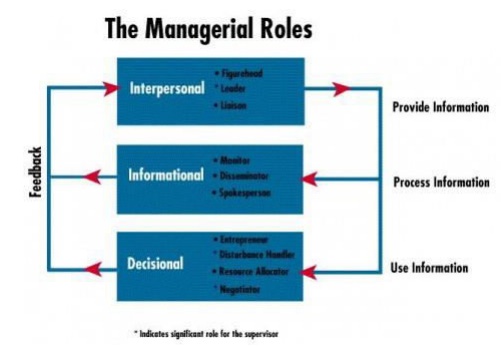
To meet the many demands of performing their functions, managers assume multiple roles. A role is an organized set of behaviours. Henry Mintzberg has identified ten roles common to the work of all managers. The ten roles are divided into three groups.
ü Interpersonal
ü Informational
ü Decisional
The
performance of managerial roles and the requirements of these roles can be
played at different times by the same manager and to different degrees
depending on the level and function of management. The ten roles are described
individually, but they form an integrated whole.
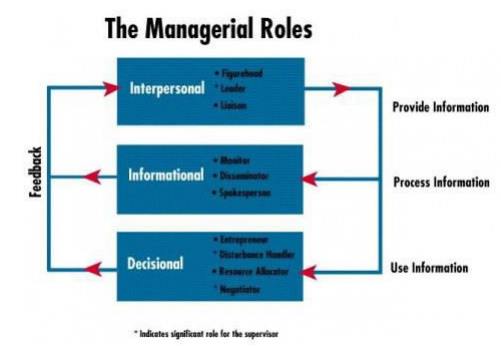
1 Interpersonal Roles
The
interpersonal roles link all managerial work together. The three interpersonal
roles are primarily concerned with interpersonal relationships.
ü Figurehead
Role: The manager represents the organization in all matters of formality. The
top level manager represents the company legally and socially to those outside
of the organization. The supervisor represents the work group to higher
management and higher management to the work group.
ü Liaison
Role: The manger interacts with peers and people outside the organization. The
top level manager uses the liaison role to gain favours and information, while
the supervisor uses it to maintain the routine flow of work.
ü The
leader Role: It defines the relationships between the manger and employees.
2 Informational Roles
The
informational roles ensure that information is provided. The three
informational roles are primarily concerned with the information aspects of
managerial work.
ü Monitor
Role: The manager receives and collects information about the operation of an
enterprise.
ü Disseminator
Role: The manager transmits special information into the organization. The top
level manager receives and transmits more information from people outside the organization
than the supervisor.
ü Spokesperson
Role: The manager disseminates the
organization’s information into its environment. Thus, the top level
manager is seen as an industry expert, while the supervisor is seen as a unit
or departmental expert.
3 Decisional Roles
The
decisional roles make significant use of the information and there are four
decisional roles.
ü Entrepreneur Role: The manager initiates change, new projects;
identify new ideas, delegate idea responsibility to others.
ü Disturbance
Handler Role: The manager deals with threats to the organization. The manager
takes corrective action during disputes or crises; resolve conflicts among
subordinates; adapt to environmental crisis.
ü Resource
Allocator Role: The manager decides who gets resources; schedule, budget set
priorities and chooses where the organization will apply its efforts.
ü Negotiator
Role: The manager negotiates on behalf of the organization. The top level
manager makes the decisions about the organization as a whole, while the
supervisor makes decisions about his or her particular work unit.
Related Topics