Chapter: Principles of Management
Classification of Environmental Factors
CLASSIFICATION OF ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS
On the
basis of the extent of intimacy with the firm, the environmental factors may be
classified into different types namely internal and external.
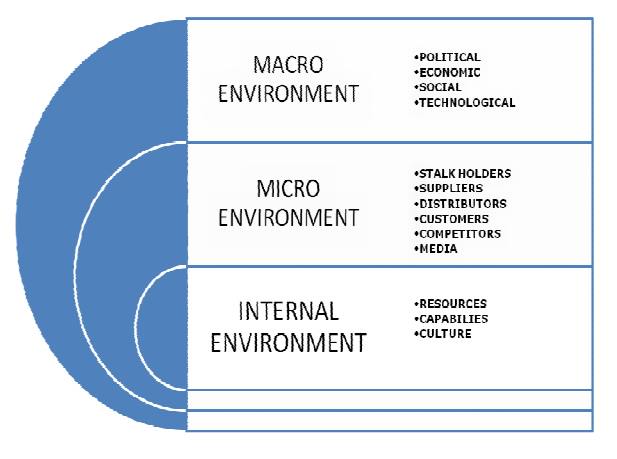
1) INTERNAL ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS
The
internal environment is the environment that has a direct impact on the
business. The internal factors are generally controllable because the company
has control over these factors. It can alter or modify these factors. The
internal environmental factors are resources, capabilities and culture.
i) Resources:
A good starting point to identify company resources is to look at
tangible, intangible and human resources.
Tangible
resources are the easiest to identify and evaluate: financial resources and
physical assets are identifies and valued in the firm’s financial statements.
Intangible
resources are largely invisible, but over time become more important to the
firm than tangible assets because they can be a main source for a competitive
advantage. Such intangible recourses include reputational assets (brands,
image, etc.) and technological assets (proprietary technology and know-how).
Human
resources or human capital are the productive services human beings offer the
firm in terms of their skills, knowledge, reasoning, and decision-making
abilities.
ii) Capabilities:
Resources
are not productive on their own. The most productive tasks require that
resources collaborate closely together within teams. The term organizational
capabilities are used to refer to a firm’s capacity for undertaking a
particular productive activity. Our interest is not in capabilities per se, but
in capabilities relative to other firms. To identify the firm’s capabilities we
will use the functional classification approach. A functional classification
identifies organizational capabilities in relation to each of the principal functional
areas.
iii) Culture:
It is the
specific collection of values and norms that are shared by people and groups in
an organization and that helps in achieving the organizational goals.
2) EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT FACTORS
It refers
to the environment that has an indirect influence on the business. The factors
are uncontrollable by the business. The two types of external environment are
micro environment and macro environment.
a) MICRO ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS
These are
external factors close to the company that have a direct impact on the
organizations process. These factors include:
i) Shareholders
Any person
or company that owns at least one share (a percentage of ownership) in a
company is known as shareholder. A shareholder may also be referred to as a
"stockholder". As organization requires greater inward investment for
growth they face increasing pressure to move from private ownership to public.
However this movement unleashes the forces of shareholder pressure on the
strategy of organizations.
ii) Suppliers
An
individual or an organization involved in the process of making a product or
service available for use or consumption by a consumer or business user is
known as supplier. Increase in raw material prices will have a knock on affect
on the marketing mix strategy of an organization. Prices may be forced up as a
result. A closer supplier relationship is one way of ensuring competitive and
quality products for an organization.
iii) Distributors
Entity that buys non-competing products
or product-lines, warehouses them, and resells them to retailers or direct to
the end users or customers is known as distributor. Most distributors provide
strong manpower and cash support to the supplier or manufacturer's promotional
efforts. They usually also provide a range of services (such as product
information, estimates, technical support, after-sales services, credit) to
their customers. Often getting products to the end customers can be a major
issue for firms. The distributors used will determine the final price of the
product and how it is presented to the end customer. When selling via
retailers, for example, the retailer has control over where the products are
displayed, how they are priced and how much they are promoted in-store. You can
also gain a competitive advantage by using changing distribution channels.
iv) Customers
A person,
company, or other entity which buys goods and services produced by another
person, company, or other entity is known as customer. Organizations survive on
the basis of meeting the needs, wants and providing benefits for their
customers. Failure to do so will result in a failed business strategy.
v) Competitors
A company
in the same industry or a similar industry which offers a similar product or
service is known as competitor. The presence of one or more competitors can
reduce the prices of goods and services as the companies attempt to gain a
larger market share. Competition also requires companies to become more
efficient in order to reduce costs. Fast-food restaurants McDonald's and Burger
King are competitors, as are Coca-Cola and Pepsi, and Wal-Mart and Target.
vi) Media
Positive
or adverse media attention on an organisations product or service can in some
cases make or break an organisation.. Consumer programmes with a wider and more
direct audience can also have a very powerful and positive impact, hforcing
organisations to change their tactics.
b) MACRO ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS
An organization's macro environment consists of nonspecific aspects in
the organization's surroundings that have the potential to affect the
organization's strategies. When compared to a firm's task environment, the
impact of macro environmental variables is less direct and the organization has
a more limited impact on these elements of the environment.
The macro
environment consists of forces that originate outside of an organization and
generally cannot be altered by actions of the organization. In other words, a
firm may be influenced by changes within this element of its environment, but
cannot itself influence the environment. The curved lines in Figure 1 indicate
the indirect influence of the environment on the organization.
Macro
environment includes political, economic, social and technological factors. A
firm considers these as part of its environmental scanning to better understand
the threats and opportunities created by the variables and how strategic plans
need to be adjusted so the firm can obtain and retain competitive advantage.
i) Political Factors
Political
factors include government regulations and legal issues and define both formal
and informal rules under which the firm must operate. Some examples include:
tax policy
employment
laws
environmental
regulations
trade
restrictions and tariffs
political
stability
Economic Factors
Economic
factors affect the purchasing power of potential customers and the firm's cost
of capital. The following are examples of factors in the macroeconomy:
economic
growth
interest
rates
exchange
rates
inflation
rate
iii) Social Factors
Social
factors include the demographic and cultural aspects of the external macro
environment. These factors affect customer needs and the size of potential
markets. Some social factors include:
health
consciousness
population
growth rate
age
distribution
career
attitudes
emphasis
on safety
Technological Factors
Technological
factors can lower barriers to entry, reduce minimum efficient production
levels, and influence outsourcing decisions. Some technological factors
include:
R&D
activity
automation
technology
incentives
rate of
technological change
Related Topics