Chapter: English
Regular & Irregular Verbs
![]()
![]() Regular
& Irregular Verbs
Regular
& Irregular Verbs
A regular verb is any verb whose conjugation follows the typical pattern, or one of the typical
patterns, of the language to which it belongs. A verb whose conjugation follows
a different pattern is called an irregular
verb.
In English, for
example, verbs such as play, enter and associate are regular, since they form their inflected parts by
adding the typical endings -s, -ing and -ed, to give forms such as plays,
entering and associated. On the other hand, verbs such as drink, hit and have are irregular, since some of their parts are not made
according to the typical pattern – drank
and drunk (not "drinked"); hit (as past tense and past participle, not "hitted") and has and had (not "haves" and "haved").
Regular Verbs
What are regular verbs?
Verbs are
a little different from most parts of speech because they can change their
form. Sometimes endings are added (like -ed or -ing) and other times the verb
itself becomes a different word (such as run
and ran).
Regular verbs are verbs that form the past tense by
adding the letter “d” or “ed” at the end.
Here’s a
brief review of simple verb tenses to make things a little clearer.
Past tense: Verbs that take place in the
past.
Present tense: Verbs that take place in the
present.
Future tense: Verbs that will take place in the
future.
Some of
the most common verbs are irregular verbs and in order to form the past tense
of those verbs, you have to memorize them. In the case of irregular verbs, it’s
not a case of simply adding a “d” or “ed” to the end of the word.
Examples of regular verbs
ask–asked back–backed
chase–chased chew–chewed
depend–depended decide–decided
employee–employed excuse–excused
There are
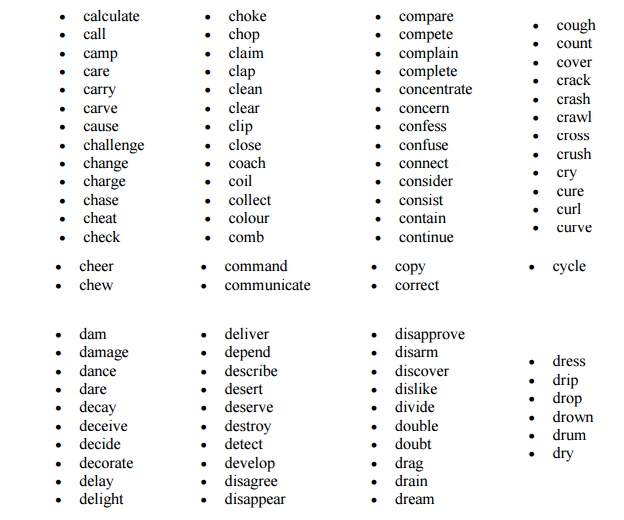
thousands of regular verbs in English. This is a list of 600 of the more common
regular verbs. Some of them were listed below:

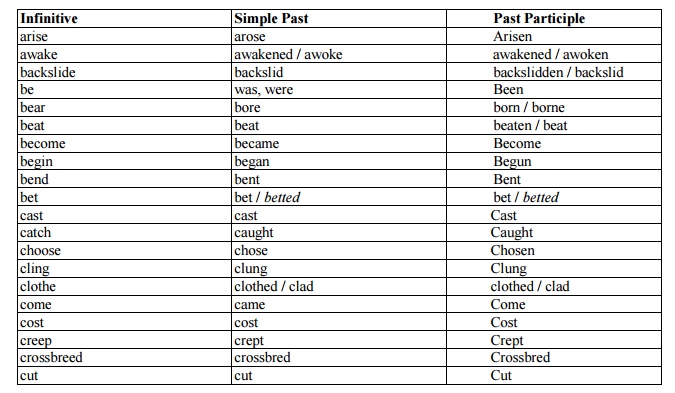
Irregular Verbs
Those
verbs that undergo substantial changes when changing forms between tenses are
irregular verbs. The changed forms of these verbs are often unrecognizably
different from the originals. For example:
PRESENT TENSE PAST TENSE
Go Went
Run Ran
Think Thought
There is
no way to tell what form an irregular verb is going to take in a changed tense;
the only option for an English speaker is to commit the changes to memory. With
practice, it will become a matter of habit.
What Is the Difference between Regular and
Irregular Verbs?
Whether
you are dealing with regular or irregular verbs in the English language, they
both have specific simple past and past participle spellings. The difference
lies in how the word is put into past tense. Simple past tense verbs always
have just one part. Past participle tense verbs have multiple parts and usually
require an auxiliary verb, such as had, has or have. With regular verbs, the
past tense simply adds an “ed” to the end of the word, with both simple past
and past particle taking the same form. However, irregular verbs are the
oddballs, the mavericks in the world of verbs; they are the
verbs that do not conform to the traditional rules. With these verbs, adding
the
“ed” is
not only incorrect, but it often sounds awkward. The patterns for irregular
verbs vary, and the simple past and past participle can end differently.
Consider the following examples:
Regular verb: I learn easily. I learned that
material yesterday. (For the verb “learn,” “learned” is both the simple past and past participle).
Irregular verb: I hurt my foot today. I hurt my
foot yesterday. (For the verb “hurt,” “hurt” is both the simple past and past participle. You would not write “I
hurted my foot yesterday”).
Different
types of irregular verbs
There are
no specific rules that dictate how the simple past and past particle verbs are
formed. Some irregular verbs all take the same form, such as put (put, put,
put). Others take different forms but have similar sounds, such as blow (blow,
blew, blown). Yet another type has simple past and past particle forms that are
identical yet differ from the present tense, such as sleep (sleep, slept,
slept). Then there are those that do not fall into any of the previous three
categories, such as go (go, went, gone). Consider the following examples:
Same form:
I put learning about irregular verbs at the top of
my to-do list today (present tense of put).
Yesterday, I put irregular verbs at the top of my
list of things to learn (simple past tense of put).
I should have put irregular verbs on my list of
things to learn much sooner (past participle tense of put).
Similar sounds:
I drink only occasionally (present tense of drink).
I drank socially last weekend (simple past tense of
drink).
I have drunk socially at most parties I attended in
college (past participle of drink).
Same simple past and past participle forms:
I make coffee as soon as I awake (present tense of
make).
I made coffee as soon as I awoke (simple past tense
of make).
I had made coffee as soon as I awoke (past
participle tense of make).
Uncategorized:
I need to go to the store (present tense of go).
I went to the store earlier (simple past tense of
go).
I have gone to the store already today (part
participle of go).
Learning irregular verbs
How do
you learn irregular verbs? Simply put, you must either memorize a rather
exhaustive list of them if they are not part of your everyday vocabulary, or
you can learn them as you go. There are many resources available to study lists
of irregular verbs. The 10 most commonly used verbs in the English language are
actually irregular (be, can, do, get, go, have, say, see, take and will).
Most
often, if English is your native language, you simply know the correct forms of
the verb for each tense of many commonly used words. In any case, when you
learn or use a verb with which you are not familiar, you should look up the
appropriate form for the tense. Over time, your knowledge of how to form the
simple past and past participle for those oddball irregular verbs expands.
Related Topics