Chapter: Genetics and Molecular Biology: Nucleic Acid and Chromosome Structure
Reading Sequence Without Dissociating Strands
Reading Sequence Without Dissociating Strands
Can the sequence of the DNA be recognized without
destroying its double helical structure? Since thousands of regulatory proteins
must bind to their cognate regulatory sequences near the genes they regulate,
it is crucial that these proteins be able to recognize their binding sequences without
requiring that the DNA strands be separated.
Sequence-dependent effects can be seen in the
slight structural dif-ferences found in crystallized oligonucleotides. It is
possible that pro-teins could utilize these structural differences and ignore the
chemical differences between the bases. For example, a protein might recognize
its correct binding site strictly by the locations of phosphates in space. The
regulator of the trp operon in Escherichia coli appears to recognize
its binding site utilizing such principles because it appears to make almost no
base-specific hydrogen bonds.
The second possibility for recognition of sequences
is to read the chemical structures of the bases. Hydrogen bonds can be made to
donors and acceptors in both the major and minor grooves as shown in
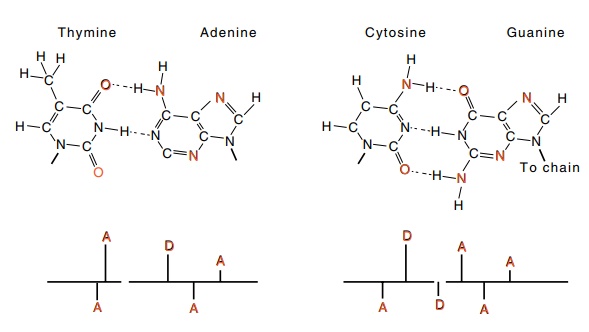
Figure
2.5 Above, T-A and C-G base pairs.
Below, schematic representation ofthe bases in which the locations of the
hydrogen bond donors (D), and acceptors (A), in the major groove are shown
above the line and those in the minor groove are shown below the line.
the schematic (Fig. 2.5). Considering the typical
flexibility in proteins, it becomes apparent that distinguishing the four base
pairs solely by the presence or absence of hydrogen bonding capabilities of the
four bases requires a minimum of two hydrogen bonds per base pair in the major
groove. A-T and T-A base pairs cannot be distinguished in the minor groove. In
nature we can expect some proteins to recognize sequence by structure
determination, some proteins to recognize sequence by hydrogen bonding to the
portions of the bases exposed in the major groove, some to utilize additional
interactions to the methyl group of thymine, and many to utilize a combination
of all these methods.
Related Topics